Page 83 - JCTR-11-4
P. 83
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research NADPH oxidase inhibition in a rodent stroke model
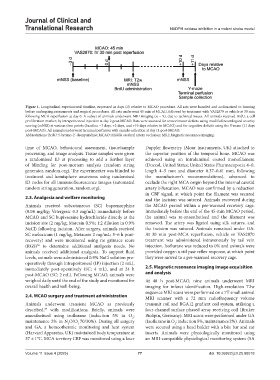
Figure 1. Longitudinal experimental timeline, expressed as days (d) relative to MCAO procedure. All rats were handled and acclimatized to housing
before undergoing assessments and surgical procedures. All rats underwent 45 min of MCAO, followed by treatment with VAS2870 or vehicle at 30 min
following MCA reperfusion at day 0. A subset of animals underwent MRI imaging (n = 9), due to technical issues. All animals received BrdU, a cell
proliferation marker, by intraperitoneal injection at day 2 post-MCAO. Rats were assessed for sensorimotor deficits using modified neurological severity
scoring (mNSS) at various time points (baseline −3 days, +2 days, and +10 days relative to MCAO) and for cognitive deficits using the Y-maze (11 days
post-MCAO). All animals underwent terminal perfusion with sample collection at day 11 post-MCAO.
Abbreviations: BrdU: 5-bromo-2’-deoxyuridine; MCAO: Middle cerebral artery occlusion; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
time of MCAO, behavioural assessment, tissue/sample Doppler flowmetry (Moor Instruments, UK) attached to
processing, and image analysis. Tissue samples were given the superior position of the temporal bone. MCAO was
a randomised ID at processing to add a further layer achieved using an intraluminal coated monofilament
of blinding for post-mortem analysis (random string (Doccol, United States; United States Pharmacopoeia 4–0,
generator, random.org). The experimenter was blinded to length 4–5 mm and diameter 0.37–0.41 mm, following
treatment and hemisphere awareness using randomised the manufacturer’s recommendations), advanced to
ID codes for all immunofluorescence images (automated occlude the right MCA origin beyond the internal carotid
random string generation, random.org). artery bifurcation. MCAO was confirmed by a reduction
in CBF signal, at which point the filament was secured
2.3. Analgesia and welfare monitoring and the incision was sutured. Animals recovered during
Animals received subcutaneous (SC) buprenorphine the MCAO period within a pre-warmed recovery cage.
(0.04 mg/kg; Vetergesic 0.3 mg/mL) immediately before Immediately before the end of the 45-min MCAO period,
MCAO and SC bupivacaine hydrochloride directly at the the animal was re-anaesthetised and the filament was
incision site (2 mg/kg; Marcain 0.5%; 1:2 dilution in 0.9% removed. The artery was ligated using silk sutures, and
NaCl) following incision. After surgery, animals received the incision was sutured. Animals remained under GA.
SC meloxicam (1 mg/kg; Metacam 2 mg/mL; 5–6 h post- At 30 min post-MCA reperfusion, vehicle or VAS2870
recovery) and were monitored using rat grimace score treatment was administered intravenously by tail vein
(RGS) to determine additional analgesia needs. No injection. Isoflurane was reduced to 0% and animals were
56
animals received additional analgesia. To support fluid provided oxygen until paw reflex response, at which point
levels, animals were administered 0.9% NaCl solution pre- they were moved to a pre-warmed recovery cage.
operatively through intraperitoneal (IP) injection (2 mL),
immediately post-operatively (SC; 4 mL), and at 24 h 2.5. Magnetic resonance imaging image acquisition
post-MCAO (SC; 2 mL). Following MCAO, animals were and analysis
weighed daily until the end of the study and monitored for At 48 h post-MCAO, nine animals underwent MRI
overall health and well-being. imaging for infarct identification. High-resolution T2w
sequence MRI scans were performed on a 7T small animal
2.4. MCAO surgery and treatment administration MRI scanner with a 72 mm radiofrequency volume
Animals underwent transient MCAO as previously transmit coil and BGA12 gradient coil system, utilising a
57
described, with modifications. Briefly, animals were four-channel surface phased array receiving coil (Bruker
anaesthetised using isoflurane (induction 5% in O ; BioSpin, Germany). MRI scans were performed under GA
2
maintenance 2% in N O/O 70/30%). During all surgery (Isoflurane in O : induction 5%, maintenance 2%). Animals
2
2
2
and GA, a homeothermic monitoring and heat system were secured using a head holder with a bite bar and ear
(Harvard Apparatus, UK) maintained body temperature at inserts. Animals were physiologically monitored using
37 ± 1°C. MCA territory CBF was monitored using a laser an MRI-compatible physiological monitoring system (SA
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 77 doi: 10.36922/jctr.25.00018