Page 88 - JCTR-11-4
P. 88
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research NADPH oxidase inhibition in a rodent stroke model
A B A B
C D
C D
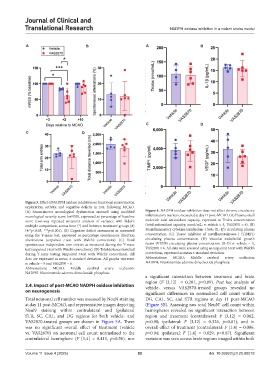
Figure 3. Effect of NADPH oxidase inhibition on functional sensorimotor,
exploration, activity, and cognitive deficits in rats, following MCAO.
(A) Sensorimotor neurological dysfunction assessed using modified Figure 4. NADPH oxidase inhibition does not affect chronic circulatory
neurological severity score (mNSS), expressed as percentage of baseline inflammatory markers, measured at day 11 post-MCAO. (A) Plasma small
score (two-way repeated measures analysis of variance with Sidak’s molecule total antioxidant capacity, expressed as Trolox concentration
multiple comparison, across time (*) and between treatment groups (#) (total antioxidant capacity; nmol/mL; n: vehicle = 4, VAS2870 = 6). (B)
(#/*p<0.05, ***p<0.001). (B) Cognitive deficit assessment as measured Proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) circulating plasma
using the Y-maze test, expressed as percentage spontaneous direction concentration. (C) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP1)
alternations (unpaired t-test with Welch’s corrections). (C) Total circulating plasma concentration. (D) Vascular endothelial growth
spontaneous independent arm entries as measured during the Y-maze factor (VEGF) circulating plasma concentration. (B-D) n: vehicle = 5,
test (unpaired t-test with Welch’s corrections). (D) Total distance travelled VAS2870 = 6. All data were assessed using an unpaired t-test with Welch’s
during Y-maze testing (unpaired t-test with Welch’s corrections). All corrections, expressed as mean ± standard deviation.
data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. All graphs represent Abbreviations: MCAO: Middle cerebral artery occlusion;
n: vehicle = 5 and VAS2870 = 6. NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
Abbreviations: MCAO: Middle cerebral artery occlusion;
NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
a significant interaction between treatment and brain
region (F [3,12] = 0.201, p=0.89). Post hoc analysis of
3.4. Impact of post-MCAO NADPH oxidase inhibition vehicle- versus VAS2870-treated groups revealed no
on neurogenesis significant differences in normalised cell count within
Total neuronal cell number was assessed by NeuN staining DG, CA1, SC, and STR regions at day 11 post-MCAO
at day 11 post-MCAO, and representative images depicting (Figure 5B). Assessing raw total NeuN cell count within
+
NeuN staining within contralateral and ipsilateral hemispheres revealed no significant interaction between
STR, SC, CA1, and DG regions for both vehicle- and region and treatment (contralateral: F [3,12] = 0.062,
VAS2870-treated groups are shown in Figure 5A. There p=0.98; ipsilateral: F [3,12] = 0.326, p=0.81), and in
was no significant overall effect of treatment (vehicle overall effect of treatment (contralateral: F [1,4] = 0.006,
vs. VAS2870) on neuronal cell count normalised to the p=0.94; ipsilateral: F [1,4] = 0.029, p=0.87). Significant
contralateral hemisphere (F [1,4] = 0.411, p=0.56), nor variation was seen across brain regions imaged within both
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 82 doi: 10.36922/jctr.25.00018