Page 92 - JCTR-11-4
P. 92
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research NADPH oxidase inhibition in a rodent stroke model
A
B C
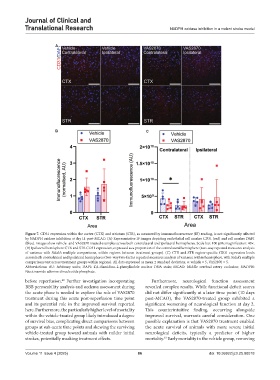
Figure 7. CD31 expression within the cortex (CTX) and striatum (STR), as measured by immunofluorescence (IF) reading, is not significantly affected
by NADPH oxidase inhibition at day 11 post-MCAO. (A) Representative IF images depicting endothelial cell marker CD31 (red) and cell marker DAPI
(blue). Images show vehicle- and VAS2870-treated examples across both contralateral and ipsilateral hemispheres. Scale bar: 100 µM; magnification: 40×.
(B) Ipsilateral hemisphere CTX and STR CD31 expression, expressed as a proportion of the contralateral hemisphere (two-way repeated measures analysis
of variance with Sidak’s multiple comparisons, within regions between treatment groups). (C) CTX and STR region-specific CD31 expression levels
across both contralateral and ipsilateral hemispheres (two-way two-factor repeated measures analysis of variance within hemisphere, with Sidak’s multiple
comparisons test across treatment groups within regions). All data expressed as mean ± standard deviation; n: vehicle = 5, VAS2870 = 5.
Abbreviations: AU: Arbitrary units; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole nuclear DNA stain; MCAO: Middle cerebral artery occlusion; NADPH:
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
48
before reperfusion. Further investigation incorporating Furthermore, neurological function assessment
BBB permeability analysis and oedema assessment during revealed complex results. While functional deficit scores
the acute phase is needed to explore the role of VAS2870 did not differ significantly at a later time point (10 days
treatment during this acute post-reperfusion time point post-MCAO), the VAS2870-treated group exhibited a
and its potential role in the improved survival reported significant worsening of neurological function at day 2.
here. Furthermore, the particularly higher level of mortality This counterintuitive finding, occurring alongside
within the vehicle-treated group likely introduced a degree improved survival, warrants careful consideration. One
of survival bias, complicating direct comparisons between possible explanation is that VAS2870 treatment enabled
groups at sub-acute time points and skewing the surviving the acute survival of animals with more severe initial
vehicle-treated group toward animals with milder initial neurological deficits, typically a predictor of higher
strokes, potentially masking treatment effects. mortality. Early mortality in the vehicle group, removing
61
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 86 doi: 10.36922/jctr.25.00018