Page 90 - JCTR-11-4
P. 90
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research NADPH oxidase inhibition in a rodent stroke model
A
B C
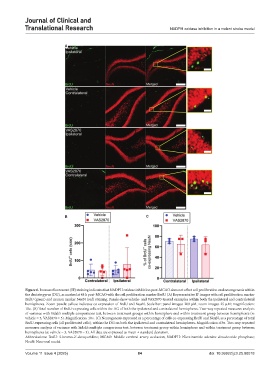
Figure 6. Immunofluorescent (IF) staining indicates that NADPH oxidase inhibition post-MCAO does not affect cell proliferation and neurogenesis within
the dentate gyrus (DG), as marked at 48 h post-MCAO with the cell proliferation marker BrdU. (A) Representative IF images with cell proliferation marker
BrdU (green) and neuron marker NeuN (red) staining. Panels show vehicle- and VAS2870-treated examples within both the ipsilateral and contralateral
hemispheres. Zoom panels: yellow indicates co-expression of BrdU and NeuN. Scale bar: panel images: 200 µM, zoom images: 25 µM; magnification:
10×. (B) Total number of BrdU-expressing cells within the DG of both the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres. Two-way repeated measures analysis
of variance with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, between treatment groups within hemisphere and within treatment group between hemispheres (n:
vehicle = 5, VAS2870 = 5). Magnification: 10×. (C) Neurogenesis expressed as a percentage of cells co-expressing BrdU and NeuN, as a percentage of total
BrdU-expressing cells (all proliferated cells), within the DG on both the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres. Magnification: 63×. Two-way repeated
measures analysis of variance with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, between treatment group within hemisphere and within treatment group between
hemispheres (n: vehicle = 3, VAS2870 = 3). All data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation.
Abbreviations: BrdU: 5-bromo-2’-deoxyuridine; MCAO: Middle cerebral artery occlusion; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate;
NeuN: Neuronal nuclei.
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 84 doi: 10.36922/jctr.25.00018