Page 79 - JCTR-11-5
P. 79
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Fibromyalgia: Examination across life domains
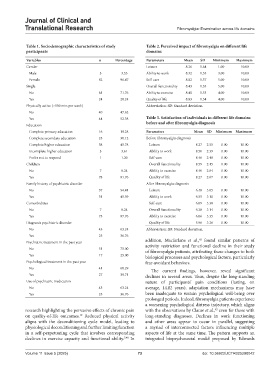
Table 1. Sociodemographic characteristics of study Table 2. Perceived impact of fibromyalgia on different life
participants domains
Variables n Percentage Parameters Mean SD Minimum Maximum
Gender Leisure 8.26 1.64 1.00 10.00
Male 3 3.53 Ability to work 8.32 1.55 3.00 10.00
Female 82 96.47 Self-care 8.82 1.37 5.00 10.00
Single Overall functionality 8.43 1.35 5.00 10.00
No 61 71.76 Ability to exercise 8.40 1.53 4.00 10.00
Yes 24 28.24 Quality of life 8.83 1.54 4.00 10.00
Physically active (>150 min per week) Abbreviation: SD: Standard deviation.
No 40 47.62
Yes 44 52.38 Table 3. Satisfaction of individuals in different life domains
before and after fibromyalgia diagnosis
Education
Complete primary education 16 19.28 Parameters Mean SD Minimum Maximum
Complete secondary education 25 30.12 Before fibromyalgia diagnosis
Complete higher education 38 45.78 Leisure 8.27 2.55 0.00 10.00
Incomplete higher education 3 3.61 Ability to work 8.50 2.39 0.00 10.00
Prefer not to respond 1 1.20 Self-care 8.46 2.48 0.00 10.00
Children Overall functionality 8.59 2.45 0.00 10.00
No 7 8.24 Ability to exercise 8.40 2.64 0.00 10.00
Yes 78 91.76 Quality of life 8.27 2.67 0.00 10.00
Family history of psychiatric disorder After fibromyalgia diagnosis
No 37 54.41 Leisure 6.48 3.05 0.00 10.00
Yes 31 45.59 Ability to work 6.55 3.10 0.00 10.00
Comorbidities Self-care 6.09 3.38 0.00 10.00
No 7 8.24 Overall functionality 6.38 3.14 0.00 10.00
Yes 75 97.76 Ability to exercise 6.06 3.35 0.00 10.00
Diagnosis psychiatric disorder Quality of life 5.96 3.26 0.00 10.00
No 43 63.24 Abbreviation: SD: Standard deviation.
Yes 25 36.76
41
Psychiatric treatment in the past year addition, Macfarlane et al., found similar patterns of
No 51 75.00 activity restriction and functional decline in their study
of fibromyalgia patients, attributing these changes to both
Yes 17 25.00 biological processes and psychological factors, particularly
Psychological treatment in the past year fear-avoidant behaviors.
No 41 60.29 The current findings, however, reveal significant
Yes 27 39.71 declines in several areas. Thus, despite the long-standing
Use of psychiatric medication nature of participants’ pain conditions (lasting, on
No 43 63.24 average, 14.82 years), adaptation mechanisms may have
Yes 25 36.76 been inadequate to sustain psychological well-being over
prolonged periods. Indeed, fibromyalgia patients experience
a worsening psychological distress trajectory, which aligns
research highlighting the pervasive effects of chronic pain with the observations by Clauw et al., even for those with
42
on quality-of-life outcomes. Reduced physical activity long-standing diagnoses. Declines in work functioning
39
aligns with the deconditioning cycle model, leading to and other areas appear to occur in parallel, suggesting
physiological deconditioning and further limiting function a myriad of interconnected factors influencing multiple
in a self-perpetuating cycle that involves corresponding aspects of life at the same time. The pattern supports an
declines in exercise capacity and functional ability. In integrated biopsychosocial model proposed by Edwards
7,40
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 73 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025290042