Page 51 - JCTR-9-5
P. 51
Iyngkaran et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2023; 9(5): 347-356 353
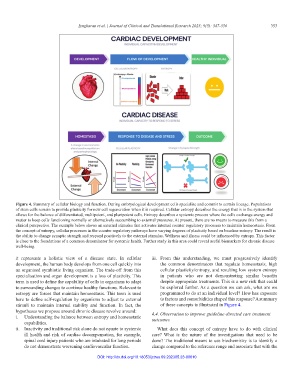
Figure 4. Summary of cellular biology and function. During embryological development cells specialise and commit to certain lineage. Populations
of stem cells remain to provide plasticity for new cell regeneration when it is required. Cellular entropy describes the energy that is in the system that
allows for the balance of differentiated, multipotent, and pluripotent cells. Entropy describes a systemic process where the cells exchange energy and
matter to keep cells functioning normally or alternatively succumbing to external pressures. At present, there are no means to measure this from a
clinical perspective. The example below shows an external stimulus that activates internal counter regulatory processes to maintain homeostasis. From
the concept of entropy, cellular processes in the counter regulatory pathways have varying degrees of plasticity based on baseline entropy. The result is
the ability to change synaptic strength and respond positively to the external stimulus. Wellness and illness could be influenced by entropy. This factor
is close to the foundations of a common denominator for systemic health. Further study in this area could reveal useful biomarkers for chronic disease
well-being.
it represents a holistic view of a disease state. In cellular iii. From this understanding, we must progressively identify
development, the human body develops from one cell quickly into the common denominators that regulate homeostasis, high
an organised symbiotic living organism. The trade-off from this cellular plasticity/entropy, and resulting low system entropy
specialisation and organ development is a loss of plasticity. This in patients who are not demonstrating similar benefits
term is used to define the capability of cells in organisms to adapt despite appropriate treatments. This is a new risk that could
to surrounding changes to continue healthy functions. Relevant to be explored further. As a question we can ask, what are we
entropy are forces that maintain homeostasis. This term is used programmed to do at an individual level? How has exposure
here to define self-regulation by organisms to adjust to external to factors and comorbidities shaped this response? A summary
stimuli to maintain internal stability and function. In fact, the of these concepts is illustrated in Figure 4.
hypotheses we propose around chronic disease revolve around: 4.4. Observation to improve guideline-directed care treatment
i. Understanding the balance between entropy and homeostatic outcomes
capabilities.
ii. Inactivity and traditional risk alone do not equate to systemic What does this concept of entropy have to do with clinical
ill health and risk of cardiac decompensation, for example, care? What is the nature of the investigations that need to be
spinal cord injury patients who are intubated for long periods done? The traditional means to use biochemistry is to identify a
do not demonstrate worsening cardiovascular function. change compared to the reference range and associate that with the
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202305.23-00010