Page 43 - MI-1-2
P. 43
Microbes & Immunity Host receptors in immunogenic cell death
a phenomenon referred to as lysosomal membrane In addition, the accumulation of ROS produced during
permeabilization (LMP). The occurrence of LMP intracellular bacterial infections causes oxidative stress and
138
is accompanied by the release of cathepsins from the damages to lysosomal membrane proteins. For instance,
lysosomal lumen, which leads to the cleavage of Bid to infections by Shigella or Chlamydia are detected by
143
generate tBid. tBid then forms pores in mitochondria NLR family member X1 (NLRX1), which localizes to
139
to trigger the release of cytochrome c (Cyto c), which mitochondria and induces the production of ROS,
144
activates the classic apoptotic pathway that ultimately leads resulting in subsequent lysosomal cell death. (4) An earlier
to caspase-3 activation and cell death 9,140 (Figure 3). study discovered that infections by L. pneumophila strains
Bacterial infections can trigger lysosomal cell death harboring wild-type rpsL such as Lp02rpsL induce
WT
through multiple mechanisms: (1) Toxins or pore- extensive lysosome damage and apoptosis in mouse bone
141
forming proteins secreted by some bacteria directly target marrow-derived macrophages, resulting in the termination
138
lysosomal membranes, leading to LMP, such as the nigericin of bacterial replication. Although the mechanism of this
from Streptomyces hygroscopicus and the pyocyanin from unique infection-induced cell death remains unknown,
145
P. aeruginosa. (2) In some context, sensing of bacterial lysosomes appear to be involved. Cellular events
9
ligands by host receptors leads to lysosomal destabilization. upstream of lysosomal membrane permeabilization await
145
The effector VepA secreted by Vibrio parahaemolyticus further investigations.
interacts with H -ATPase and such binding disrupts the 4. Conclusion and perspectives
+
integrity of lysosomal membranes and induces LMP. (3)
142
In light of their critical roles in the innate immune
response and inflammation, the PRRs have been explored
as potential drug targets for a variety of diseases in the
past two decades, including bacterial and viral infectious
diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancers. For
146
instance, given the critical role of NLRs in inflammasome
formation and regulation of IL-1β and IL-18, NLRP3 has
been targeted for the development of anti-inflammatory
drugs. Inhibitors of the NLRP3 inflammasome are being
applied to relieve excessive inflammation, such as gout,
type 2 diabetes, and atherosclerosis. Furthermore,
62
agonists of TLR7 and TLR9 have been explored for their
potential to enhance antitumor immunity by promoting
the activation of dendritic cells and B cells. In addition, a
26
recent study demonstrated that nanoparticle-encapsulated
TLR9 agonists effectively activate plasmacytoid
dendritic cells to secrete factors that enhance antigen
presentation by myeloid dendritic cells, underscoring
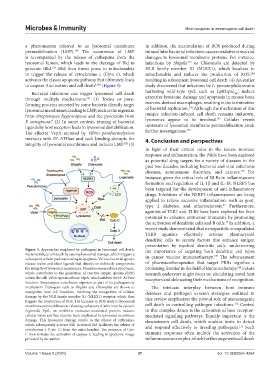
Figure 3. Approaches employed by pathogens in lysosomal cell death. the importance of targeting both dendritic cell types
Bacteria induce cell death by causing lysosomal damage, which triggers a in cancer vaccine immunotherapy. The advancement
147
subsequent cellular pathway leading to apoptosis. Various bacterial species
release toxins and other ligands that directly or indirectly compromise of pharmacotherapeutics that target PRRs signifies a
148
the integrity of lysosomal membranes. Pseudomonas produces pyocyanin, promising frontier in the field of immunotherapy. Future
which contributes to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) research endeavors might focus on elucidating novel host
within the cell. Vibrio species release VepA, which inhibits the H ATPase receptors and delineating their mechanisms of recognition.
+
function. Streptomyces contributes nigericin as part of its pathogenicity
mechanism. Pathogens such as Shigella and Chlamydia are shown to The intricate interplay between host immune
manipulate host cell functions, involving the recognition of cellular defenses and pathogen evasion strategies outlined in
damage by the NLR family member X1 (NLRX1) receptor, which then this review emphasizes the pivotal role of immunogenic
triggers the production of ROS. The increase in ROS leads to lysosomal 112
membrane permeabilization, releasing cathepsins (CtsB) into the cytosol. cell death in controlling pathogen infections. Central
Legionella RpsL, an antibiotic resistance-associated protein, induces to this complex dance is the activation of host receptor-
cellular stress and has recently been implicated in lysosomal membrane mediated signaling pathways. Equally important is the
damage. This lysosomal damage results in the release of cathepsins, downstream cell death, which enables hosts to detect
which subsequently activate Bid. Activated Bid facilitates the release of and respond effectively to invading pathogens. Such
112
cytochrome c (Cyto C) from the mitochondria. The presence of Cyto
C then initiates the activation of caspase 3, leading to apoptosis. Image immune responses often include the activation of the
provided by the author. inflammasome complex, which further augments cell death
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 37 doi: 10.36922/mi.4264