Page 180 - MI-2-3
P. 180
Microbes & Immunity A novel anti-EphB2 monoclonal antibody for flow cytometry
A
B
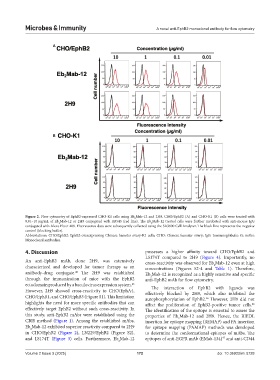
Figure 2. Flow cytometry of EphB2-expressed CHO-K1 cells using Eb Mab-12 and 2H9. CHO/EphB2 (A) and CHO-K1 (B) cells were treated with
2
0.01–10 μg/mL of Eb Mab-12 or 2H9 conjugated with RB545 (red line). The Eb Mab-12 treated cells were further incubated with anti-mouse IgG
2
2
conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488. Fluorescence data were subsequently collected using the SA3800 Cell Analyzer. The black line represents the negative
control (blocking buffer).
Abbreviations: CHO/EphB2: EphB2-overexpressing Chinese hamster ovary-K1 cells; CHO: Chinese hamster ovary; IgG: Immunoglobulin G; mAbs:
Monoclonal antibodies.
4. Discussion possesses a higher affinity toward CHO/EphB2 and
LS174T compared to 2H9 (Figure 4). Importantly, no
An anti-EphB2 mAb, clone 2H9, was extensively cross-reactivity was observed for Eb Mab-12 even at high
characterized and developed for tumor therapy as an concentrations (Figures S2-4 and Table 1). Therefore,
2
antibody-drug conjugate. The 2H9 was established Eb Mab-12 is recognized as a highly sensitive and specific
46
2
through the immunization of mice with the EphB2 anti-EphB2 mAb for flow cytometry.
ectodomain produced by a baculovirus expression system.
46
The interaction of EphB2 with ligands was
However, 2H9 showed cross-reactivity to CHO/EphA4, effectively blocked by 2H9, which also inhibited the
CHO/EphB1, and CHO/EphB3 (Figure S1). This limitation autophosphorylation of EphB2. However, 2H9 did not
46
highlights the need for more specific antibodies that can affect the proliferation of EphB2-positive tumor cells.
46
effectively target EphB2 without such cross-reactivity. In The identification of the epitope is essential to assess the
this study, anti-EphB2 mAbs were established using the properties of Eb Mab-12 and 2H9. Hence, the RIEDL
2
CBIS method (Figure 1). Among the established mAbs, insertion for epitope mapping (REMAP) and PA insertion
Eb Mab-12 exhibited superior reactivity compared to 2H9 for epitope mapping (PAMAP) methods was developed
2
in CHO/EphB2 (Figure 2), LN229/EphB2 (Figure S2), to determine the conformational epitopes of mAbs. The
and LS174T (Figure 3) cells. Furthermore, Eb Mab-12 epitopes of anti-EGFR mAb (EMab-134) and anti-CD44
47
2
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 172 doi: 10.36922/mi.5728