Page 27 - MI-2-3
P. 27
Microbes & Immunity Correlation between VZV and cancer
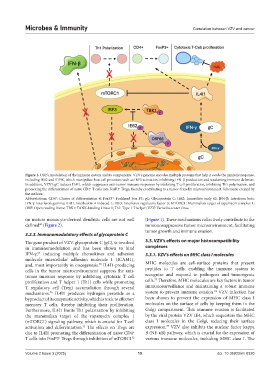
Figure 1. ORF’s modulation of the immune system and its components. VZV’s genome encodes multiple proteins that help it evade the immune response,
including IE62 and STPK, which manipulate host cell processes such as IRF3 activation, inhibiting IFN-β production and weakening immune defenses.
In addition, VZV’s gC induces IL4I1, which suppresses anti-tumor immune responses by inhibiting T cell proliferation, inhibiting Th1 polarization, and
promoting the differentiation of naive CD4 T cells into FoxP3 Tregs, thereby contributing to a tumor-friendly microenvironment. Schematic created by
+
+
the authors.
Abbreviations: CD4 : Cluster of differentiation 4; FoxP3 : Forkhead box P3; gC: Glycoprotein C; IE62: Immediate early 62; IFN-β: Interferon beta;
+
+
IFN-γ: Interferon gamma; IL4I1: Interleukin-4-induced-1; IRF3: Interferon regulatory factor 3; MTORC1: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1;
ORF: Open reading frame; TBK1: TANK-binding kinase 1; Th1: Type 1 T helper; VZV: Varicella-zoster virus.
on mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells are not well (Figure 1). These mechanisms collectively contribute to the
defined (Figure 2). immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, facilitating
68
tumor growth and immune evasion.
3.2.3. Immunomodulatory effects of glycoprotein C
The gene product of VZV, glycoprotein C (gC), is involved 3.3. VZV’s effects on major histocompatibility
in immunomodulation and has been shown to bind complexes
IFN-γ, inducing multiple chemokines and adhesion 3.3.1. VZV’s effects on MHC class I molecules
69
molecule intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1),
and, most importantly in oncogenesis. IL4I1-producing MHC molecules are cell-surface proteins that present
70
cells in the tumor microenvironment suppress the anti- peptides to T cells, enabling the immune system to
tumor immune response by inhibiting cytotoxic T cell recognize and respond to pathogens and tumorigenic
73
proliferation and T helper 1 (Th1) cells while promoting cells. Therefore, MHC molecules are key factors in tumor
T regulatory cell (Treg) accumulation through several immunosurveillance and maintaining a robust immune
74
mechanisms. IL4I1 produces hydrogen peroxide as a system to prevent immune evasion. VZV infection has
70
byproduct of its enzymatic activity, which is toxic to effector/ been shown to prevent the expression of MHC class I
memory T cells, thereby inhibiting their proliferation. molecules on the surface of cells by keeping them in the
Furthermore, IL4I1 limits Th1 polarization by inhibiting Golgi compartment. This immune evasion is facilitated
the mammalian target of the rapamycin complex 1 by the viral protein VZV IE4, which sequesters the MHC
(mTORC1) signaling pathway, which is crucial for T-cell class I molecules in the Golgi, reducing their surface
75
activation and differentiation. The effects on Tregs are expression. VZV also inhibits the nuclear factor kappa
71
due to IL4I1 promoting the differentiation of naive CD4 B (NF-κB) pathway, which is crucial for the expression of
+
T cells into FoxP3 Tregs through inhibition of mTORC1 various immune molecules, including MHC class I. The
+
72
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 19 doi: 10.36922/mi.8320