Page 106 - MI-2-4
P. 106
Microbes & Immunity Brachyspira pilosicoli novel outer membrane proteins
A B C D E
F G H I J
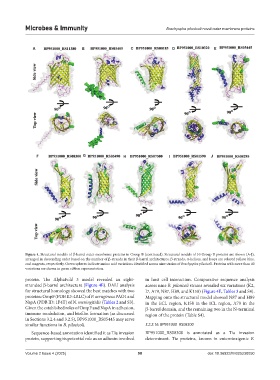
Figure 4. Structural models of β-barrel outer membrane proteins in Group B (continued). Structural models of 10 Group B proteins are shown (A-J),
arranged in descending order based on the number of β-strands in their β-barrel architectures. β-strands, α-helices, and loops are colored yellow, blue,
and magenta, respectively. Green spheres indicate amino acid variations identified across nine strains of Brachyspira pilosicoli. Proteins with more than 40
variations are shown in green ribbon representation.
protein. The AlphaFold 3 model revealed an eight- in host cell interaction. Comparative sequence analysis
stranded β-barrel architecture (Figure 4E). DALI analysis across nine B. pilosicoli strains revealed six variations (K2,
for structural homology showed the best matches with two I7, A79, N87, H89, and K158) (Figure 4E, Tables 3 and S4).
proteins: OmpF (PDB ID: 4RLC) of P. aeruginosa PAO1 and Mapping onto the structural model showed N87 and H89
NspA (PDB ID: 1P4T) of N. meningitidis (Tables 2 and S3). in the ECL region, K158 in the ICL region, A79 in the
Given the established roles of OmpF and NspA in adhesion, β-barrel domain, and the remaining two in the N-terminal
immune modulation, and biofilm formation (as discussed region of the protein (Table S4).
in Sections 3.2.4 and 3.2.5), BP951000_RS05445 may serve
similar functions in B. pilosicoli. 3.2.2.16. BP951000_RS08300
Sequence-based annotation identified it as Tia invasion BP951000_RS08300 is annotated as a Tia invasion
protein, supporting its potential role as an adhesin involved determinant. Tia proteins, known in enterotoxigenic E.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 98 doi: 10.36922/MI025230050