Page 77 - MSAM-3-1
P. 77
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Alumina platelets additive manufacturing
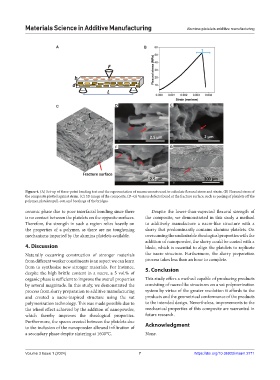
A B
C D E
F G
Figure 4. (A) Set-up of three-point bending test and the representation of measurements used to calculate flexural stress and strain. (B) Flexural stress of
the composite plotted against strain. (C) 3D image of the composite. (D–G) Various defects found at the fracture surface, such as peeling of platelets off the
polymer, platelets pull-out, and breakage of the bridges.
ceramic phase due to poor interfacial bonding since there Despite the lower-than-expected flexural strength of
is no contact between the platelets on the opposite surfaces. the composite, we demonstrated in this study a method
Therefore, the strength in such a region relies heavily on to additively manufacture a nacre-like structure with a
the properties of a polymer, as there are no toughening slurry that predominantly contains alumina platelets. On
mechanisms imparted by the alumina platelets available. overcoming the undesirable rheological properties with the
addition of nanopowder, the slurry could be coated with a
4. Discussion blade, which is essential to align the platelets to replicate
Naturally occurring construction of stronger materials the nacre structure. Furthermore, the slurry preparation
from different weaker constituents is an aspect we can learn process takes less than an hour to complete.
from to synthesize new stronger materials. For instance, 5. Conclusion
despite the high brittle content in a nacre, a 5 vol.% of
organic phase is sufficient to improve the overall properties This study offers a method capable of producing products
by several magnitude. In this study, we demonstrated the consisting of nacre-like structures on a vat polymerization
process from slurry preparation to additive manufacturing system by virtue of the greater resolution it affords to the
and created a nacre-inspired structure using the vat products and the geometrical conformance of the products
polymerization technology. This was made possible due to to the intended design. Nevertheless, improvements to the
the wheel effect achieved by the addition of nanopowder, mechanical properties of this composite are warranted in
which thereby improves the rheological properties. future research.
Furthermore, the spaces created between the platelets due
to the inclusion of the nanopowder allowed infiltration of Acknowledgment
a secondary phase despite sintering at 1600°C. None.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2711