Page 82 - MSAM-3-1
P. 82
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Bioactive hydrogels for 3D bioprinting
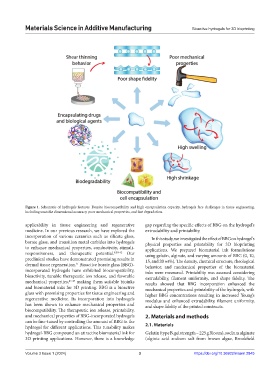
Figure 1. Schematic of hydrogels features. Despite biocompatibility and high encapsulation capacity, hydrogels face challenges in tissue engineering,
including unstable dimensional accuracy, poor mechanical properties, and fast degradation.
applicability in tissue engineering and regenerative gap regarding the specific effects of BBG on the hydrogel’s
medicine. In our previous research, we have explored the extrudability and printability.
incorporation of various ceramics such as silicate glass, In this study, we investigated the effect of BBG on hydrogel’s
borate glass, and transition metal carbides into hydrogels physical properties and printability for 3D bioprinting
to enhance mechanical properties, conductivity, stimuli- applications. We prepared biomaterial ink formulations
responsiveness, and therapeutic potential. 8,38-42 Our using gelatin, alginate, and varying amounts of BBG (0, 10,
preclinical studies have demonstrated promising results in 15, and 20 wt%). The density, chemical structure, rheological
dermal tissue regeneration. Bioactive borate glass (BBG)- behavior, and mechanical properties of the biomaterial
21
incorporated hydrogels have exhibited biocompatibility, inks were measured. Printability was assessed considering
bioactivity, tunable therapeutic ion release, and favorable extrudability, filament uniformity, and shape fidelity. The
mechanical properties, 43-49 making them suitable bioinks results showed that BBG incorporation enhanced the
and biomaterial inks for 3D printing. BBG is a bioactive mechanical properties and printability of the hydrogels, with
glass with promising properties for tissue engineering and higher BBG concentrations resulting in increased Young’s
regenerative medicine. Its incorporation into hydrogels modulus and enhanced extrudability, filament uniformity,
has been shown to enhance mechanical properties and and shape fidelity of the printed constructs.
biocompatibility. The therapeutic ion release, printability,
and mechanical properties of BBG-incorporated hydrogels 2. Materials and methods
can be fine-tuned by controlling the amount of BBG in the
hydrogel for different applications. This tunability makes 2.1. Materials
hydrogel-BBG compound an attractive biomaterial ink for Gelatin (type B, gel strength ~ 225 g Bloom), sodium alginate
3D printing applications. However, there is a knowledge (alginic acid sodium salt from brown algae, Brookfield
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2845