Page 134 - MSAM-4-2
P. 134
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Mouthguards: Disinfection versus properties changes
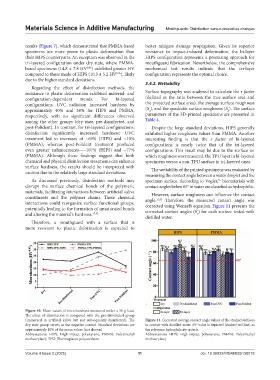
results (Figure 7), which demonstrated that PMMA-based better mitigate damage propagation. Given its superior
specimens are more prone to plastic deformation than resistance to impact-induced deformation, the bi-layer
their HIPS counterparts. An exception was observed in the HIPS configuration represents a promising approach for
tri-layered configuration under dry state, where PMMA- mouthguard fabrication. Nevertheless, the comprehensive
based specimens (14.8 ± 7.8 HV ) exhibited greater HV mechanical test results indicate that the tri-layer
0.05
compared to those made of HIPS (10.3 ± 5.2 HV ), likely configuration represents the optimal choice.
0.05
due to the higher standard deviations.
3.4.2. Wettability
Regarding the effect of disinfection methods, the
resistance to plastic deformation exhibited material- and Surface topography was analyzed to calculate the r factor
configuration-dependent trends. For bi-layered (defined as the ratio between the true surface area and
configurations, UVC radiation increased hardness by the projected surface area), the average surface roughness
approximately 40% and 38% for HIPS and PMMA, (S ), and the quadratic surface roughness (S ). The surface
q
a
respectively, with no significant differences observed parameters of the 3D-printed specimens are presented in
among the other groups (dry state, pre-disinfected, and Table 4.
post-Polident). In contrast, for tri-layered configurations, Despite the large standard deviations, HIPS generally
disinfection significantly increased hardness: UVC exhibited higher roughness values than PMMA. Another
treatment led to increases of ~69% (HIPS) and ~10% interesting finding is that the r factor of bi-layered
(PMMA), whereas post-Polident treatment produced configurations is nearly twice that of the tri-layered
even greater enhancements—~107% (HIPS) and ~77% configurations. This result may be due to the surface on
(PMMA). Although these findings suggest that both which roughness was measured: the TPU layer in bi-layered
chemical and physical disinfection treatments can enhance specimens versus a non-TPU surface in tri-layered ones.
surface hardness, the results should be interpreted with The wettability of the printed specimens was evaluated by
caution due to the relatively large standard deviations.
measuring the contact angle between a water droplet and the
As discussed previously, disinfection methods may specimen surface. According to Vogler, biomaterials with
55
disrupt the surface chemical bonds of the polymeric contact angles below 65° in water are classified as hydrophilic.
materials, facilitating interactions between artificial saliva However, surface roughness can influence the contact
constituents and the polymer chains. These chemical angle. 11,55 Therefore, the measured contact angle was
interactions could reorganize surface functional groups, corrected using Wenzel’s equation. Figure 11 presents the
potentially leading to the formation of unsaturated bonds corrected contact angles (θ ) for each surface tested with
and altering the material’s hardness. 17,52 r
distilled water.
Therefore, a mouthguard with a surface that is
more resistant to plastic deformation is expected to
Figure 10. Mean values of microhardness measured under a 50 g load.
The effect of disinfection is compared with the pre-disinfected group
(immersed in artificial saliva but not subsequently disinfected). The Figure 11. Corrected average contact angle values of the studied surfaces
dry state group serves as the negative control. Standard deviations are in contact with distilled water. 65° value is depicted (dashed red line) as
approximately 10% of the mean values (not shown) the reference hydrophilicity criteria
Abbreviations: HIPS: High-impact polystyrene; PMMA: Poly(methyl Abbreviations: HIPS: High-impact polystyrene; PMMA: Poly(methyl
methacrylate); TPU: Thermoplastic polyurethane methacrylate)
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 11 doi: 10.36922/MSAM025130018