Page 64 - OR-1-3
P. 64
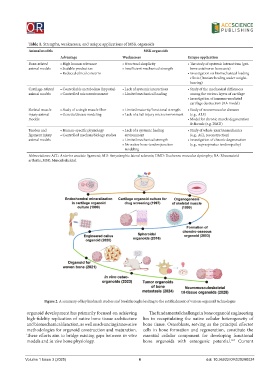
Table 1. Strengths, weaknesses, and unique applications of MSK organoids
Animal models MSK organoids
Advantage Weaknesses Unique application
Bone-related • High human relevance • Structural simplicity • The study of systemic interactions (gut-
animal models • Scalable production • Insufficient mechanical strength bone axis/nerve-bone axis)
• Reduced ethical concerns • Investigation on biomechanical loading
effects (fracture healing under weight-
bearing)
Cartilage-related • Controllable metabolism (hypoxia) • Lack of systemic interactions • Study of the mechanical differences
animal models • Controlled microenvironment • Limited mechanical loading among the various layers of cartilage
• Investigation of immune-mediated
cartilage destruction (RA model)
Skeletal muscle • Study of a single muscle fiber • Limited maturity/functional strength • Study of neuromuscular diseases
injury animal • Genetic/disease modeling • Lack of a full injury microenvironment (e.g., ALS)
models • Model for chronic muscle degeneration
& fibrosis (e.g. DMD)
Tendon and • Human-specific physiology • Lack of a systemic healing • Study of whole-joint biomechanics
ligament injury • Controlled mechanobiology studies environment (e.g., ACL reconstruction)
animal models • Limited mechanical strength • Investigation of chronic degeneration
• No native bone-tendon junction (e.g., supraspinatus tendinopathy)
modeling
Abbreviations: ACL: Anterior cruciate ligament; ALS: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; DMD: Duchenne muscular dystrophy; RA: Rheumatoid
arthritis; MSK: Musculoskeletal.
Figure 2. A summary of key landmark studies and breakthroughs leading to the establishment of various organoid technologies
organoid development has primarily focused on achieving The fundamental challenge in bone organoid engineering
high-fidelity replication of native bone tissue architecture lies in recapitulating the native cellular heterogeneity of
and biomechanical function, as well as advancing innovative bone tissue. Osteoblasts, serving as the principal effector
methodologies for organoid construction and maturation. cells in bone formation and regeneration, constitute the
These efforts aim to bridge existing gaps between in vitro essential cellular component for developing functional
models and in vivo bone physiology. bone organoids with osteogenic potential. Current
124
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/OR025280024