Page 61 - OR-1-3
P. 61
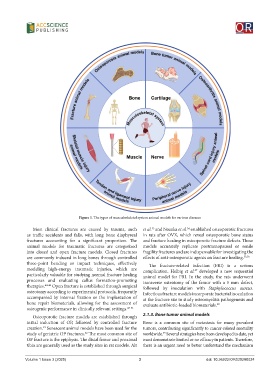
Figure 1. The types of musculoskeletal system animal models for various diseases
Most clinical fractures are caused by trauma, such et al. and Nozaka et al. established osteoporotic fractures
53
54
as traffic accidents and falls, with long bone diaphyseal in rats after OVX, which reveal osteoporotic bone status
fractures accounting for a significant proportion. The and fracture healing in osteoporotic fracture defects. These
animal models for traumatic fractures are categorized models accurately replicate postmenopausal or senile
into closed and open fracture models. Closed fractures fragility fractures and are indispensable for investigating the
are commonly induced in long bones through controlled effects of anti-osteoporotic agents on fracture healing. 55,56
three-point bending or impact techniques, effectively The fracture-related infection (FRI) is a serious
modeling high-energy traumatic injuries, which are complication. Helbig et al. developed a new sequential
57
particularly valuable for studying normal fracture healing animal model for FRI. In the study, the rats underwent
processes and evaluating callus formation-promoting transverse osteotomy of the femur with a 5 mm defect,
therapies. 44-46 Open fracture is established through surgical followed by inoculation with Staphylococcus aureus.
osteotomy according to experimental protocols, frequently Infectious fracture models incorporate bacterial inoculation
accompanied by internal fixation or the implantation of at the fracture site to study osteomyelitis pathogenesis and
bone repair biomaterials, allowing for the assessment of evaluate antibiotic-loaded biomaterials. 58
osteogenic performance in clinically relevant settings. 47-51
Osteoporotic fracture models are established through 2.1.3. Bone tumor animal models
initial induction of OP, followed by controlled fracture Bone is a common site of metastasis for many prevalent
creation. Senescent animal models have been used for the tumors, contributing significantly to cancer-related mortality
43
study of geriatric OP fractures. The most common site of worldwide. Several strategies have been developed to date, yet
59
52
OP fracture is the epiphysis. The distal femur and proximal most demonstrate limited or no efficacy in patients. Therefore,
tibia are generally used as the study sites in rat models. Alt there is an urgent need to better understand the mechanism
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/OR025280024