Page 70 - OR-1-3
P. 70
A B
C
D E
F G
H I J K
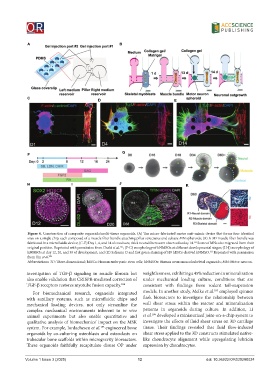
Figure 4. Construction of composite organoids/multi-tissue organoids. (A) The micro-fabricated motor unit-mimic device that forms four identical
sites on a single chip, each composed of a muscle fiber bundle attaching pillar structures and culture MN spheroids; (B) A 3D muscle fiber bundle was
fabricated in a microfluidic device; (C-E) Day 1, 4, and 14 of coculture, thick neural fibers were observed at day 14. Some of MNs also migrated from their
165
original position. Reprinted with permission from Osaki et al. ; (F-G) morphology of hNMSOs at different developmental stages; (H-J) morphology of
165
hNMSOs at day 12, 20, and 38 of development; and (K) Safranin O and fast green staining of H9 hESCs-derived hNMSO. Reprinted with permission
121
from Yin et al. 121
Abbreviations: 3D: Three-dimensional; hESCs: Human embryonic stem cells; hNMSOs: Human neuromusculoskeletal organoids; MN: Motor neuron.
investigation of TGF-β signaling in muscle fibrosis but weightlessness, exhibiting a 45% reduction in mineralization
also enable validation that CRISPR-mediated correction of under mechanical loading culture, conditions that are
TGF-β receptors restores myotube fusion capacity. 184 consistent with findings from rodent tail-suspension
185
For biomechanical research, organoids integrated models. In another study, Melke et al. employed spinner
with auxiliary systems, such as microfluidic chips and flask bioreactors to investigate the relationship between
mechanical loading devices, not only streamline the wall shear stress within the reactor and mineralization
complex mechanical environments inherent to in vivo patterns in organoids during culture. In addition, Li
186
animal experiments but also enable quantitative and et al. developed a miniaturized joint-on-a-chip system to
qualitative analysis of biomechanics’ impact on the MSK investigate the effects of fluid shear stress on 3D cartilage
system. For example, Iordachescu et al. engineered bone tissue. Their findings revealed that fluid flow-induced
133
organoids by co-culturing osteoblasts and osteoclasts on shear stress applied to the 3D constructs stimulated native-
trabecular bone scaffolds within microgravity bioreactors. like chondrocyte alignment while upregulating lubricin
These organoids faithfully recapitulate disuse OP under expression by chondrocytes.
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 12 doi: 10.36922/OR025280024