Page 11 - TD-2-3
P. 11
Tumor Discovery Targeted drug delivery systems for the treatment of tumors
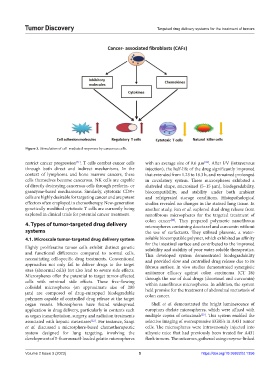
Figure 3. Stimulation of cell-mediated responses by cancerous cells.
[21]
restrict cancer progression . T cells combat cancer cells with an average size of 9.6 μm . After I/V (intravenous
[23]
through both direct and indirect mechanisms. In the injection), the half-life of the drug significantly improved
context of lymphoma and bone marrow cancers, these that extended from 1.23 to 18.3 h, and remained prolonged
cells themselves become cancerous. NK cells are capable in circulatory system. These microspheres exhibited a
of directly destroying cancerous cells through perforin- or shriveled shape, microsized (5–15 μm), biodegradability,
granzyme-based mechanisms. Similarly, cytotoxic CD8+ biocompatibility, and stability under both ambient
cells are highly desirable for targeting cancer and are potent and refrigerated storage conditions. Histopathological
effectors often employed in chemotherapy. New-generation studies revealed no changes in the stained lung tissue. In
genetically modified cytotoxic T cells are currently being another study, Fan et al. explored dual drug release from
explored in clinical trials for potential cancer treatment. nanofibrous microspheres for the targeted treatment of
colon cancer . They prepared polymeric nanofibrous
[24]
4. Types of tumor-targeted drug delivery microspheres containing docetaxel and curcumin without
systems the use of surfactants. They utilized pluronic, a water-
4.1. Microscale tumor-targeted drug delivery system soluble biocompatible polymer, which exhibited an affinity
for the intestinal surface and contributed to the improved
Highly proliferative tumor cells exhibit distinct genetic solubility and stability of poor water-soluble therapeutics.
and functional differences compared to normal cells, This developed system demonstrated biodegradability
necessitating cell-specific drug treatments. Conventional and provided slow and controlled drug release due to its
approaches not only fail to deliver drugs to the target fibrous surface. In vivo studies demonstrated synergistic
sites (abnormal cells) but also lead to severe side effects. antitumor efficacy against colon carcinoma (CT 26)
Microspheres offer the potential to target tumor-affected through the use of dual drugs (docetaxel and curcumin)
cells with minimal side effects. These free-flowing within nanofibrous microspheres. In addition, the system
colloidal microspheres (an approximate size of 200 held promise for the treatment of abdominal metastasis of
μm) are composed of drug-entrapped biodegradable colon cancer.
polymers capable of controlled drug release at the target
organ vessels. Microspheres have found widespread Shell et al. demonstrated the bright luminescence of
application in drug delivery, particularly in contexts such europium chelate microspheres, which were affixed with
as organ transplantation, surgery, and radiation treatments multiple copies of cetuximab . This system enabled the
[25]
[22]
associated with hepatic metastases . For instance, Sangi selective imaging of overexpressive EGRFs in A431 tumor
et al. discussed a microsphere-based chemotherapeutic cells. The microspheres were intravenously injected into
system designed for lung targeting, involving the athymic mice that had previously been treated for A431
development of 5-fluorouracil-loaded gelatin microspheres flank tumors. The outcomes, gathered using enzyme-linked
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.1356