Page 11 - TD-3-1
P. 11
Tumor Discovery Haplotype and LD of BRCA genes in GBM
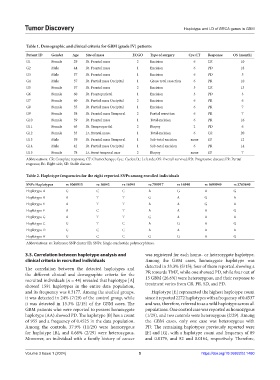
Table 1. Demographic and clinical criteria for GBM (grade IV) patients
Patient ID Gender Age Site of mass ECGO Type of surgery Cyc.CT Response OS (month)
G1 Female 29 Rt. Frontal mass 2 Excision 6 CR 10
G2 Male 44 Rt. Frontal mass 1 Excision 6 PD 18
G3 Male 37 Rt. Frontal mass 1 Excision 6 PD 5
G4 Male 57 Rt. Partial mass Occipital 1 Gross total resection 6 PR 10
G5 Female 57 Rt. Frontal mass 2 Excision 3 CR 13
G6 Female 60 Rt. Frontoparietal 1 Excision 3 PD 3
G7 Female 60 Rt. Partial mass Occipital 2 Excision 6 PR 6
G8 Female 55 Rt. Partial mass Occipital 1 Excision 6 PR 7
G9 Female 38 Rt. Frontal mass Temporal 2 Partial resection 6 PR 7
G10 Female 59 Rt. Frontal mass 1 Total excision 6 PR 16
G11 Female 65 Rt. Tempropartial 2 Biopsy 2 PD 6
G12 Female 33 Lt. Frontal mass. 1 Total excision 6 CR 20
G13 Male 39 Rt. Frontal mass Temporal 1 Sub-total excision none SD 12
G14 Male 42 Rt. Partial mass Occipital 1 Sub-total excision 6 PR 14
G15 Female 78 Lt. Front temporal mas 2 Biopsy none SD 7
Abbreviations: CR: Complete response; CT: Chemotherapy; Cyc.: Cycles; Lt.: Left side; OS: Overall survival; PD: Progressive disease; PR: Partial
response; Rt.: Right side; SD: Stable disease.
Table 2. Haplotype frequencies for the eight reported SNPs among enrolled individuals
SNPs Haplotypes rs 1060915 rs 16042 rs 16941 rs 799917 rs 16940 rs 1699949 rs 3765640
Haplotype A G C C A G A G
Haplotype B A T T G A G A
Haplotype E A T T A A G A
Haplotype F A C T A A A G
Haplotype G A T T G A A A
Haplotype C G T C A G A G
Haplotype D G C C A A A A
Haplotype H G C C G G A G
Abbreviations: rs: Reference SNP cluster ID; SNPs: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms.
3.3. Correlation between haplotype analysis and was registered for each homo- or heterozygote haplotype.
clinical criteria in recruited individuals Among the GBM cases, homozygote haplotype was
detected in 33.3% (5/15); four of them reported showing a
The correlation between the detected haplotypes and
the different clinical and demographic criteria for the PR towards TMZ, while one showed PD, while four out of
recruited individuals (n = 44) revealed that haplotype [A] 15 GBM (26.6%) were heterozygous, and their response to
showed 1591 haplotypes in the entire data population, treatment varies from CR, PR, SD, and PD.
and its frequency was 0.3177. Among the studied groups, Haplotype [E] represented the highest haplotype count
it was detected in 24% (7/29) of the control group, while since it reported 2272 haplotypes with a frequency of 0.4537
it was detected in 13.3% (2/15) of the GBM cases. The and was, therefore, referred to as a wild haplotype across all
GBM patients who were reported to possess homozygote populations. One control case was reported as homozygous
haplotype (AA) showed PD. The haplotype [B] has a count (1/29), and two controls were heterozygous (2/29). Among
of 955 and a frequency of 0.4525 in the data population. the GBM cases, only one case was heterozygous with
Among the controls, 37.9% (11/29) were homozygous PD. The remaining haplotypes previously reported were
for haplotype [B], and 0.68% (2/29) were heterozygous. [F] and [G], with a haplotype count and frequency of 89
Moreover, an individual with a family history of cancer and 0.0179, and 82 and 0.0164, respectively. Therefore,
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.1480