Page 117 - TD-3-1
P. 117
Tumor Discovery Inflammatory orbital pseudotumors
Congenital lesions, particularly lymphangiomas and A B
dermoid cysts, may exhibit sporadic symptoms that
resemble IDO or develop an inflammatory component.
6
In addition, the extra-scleral expansion of primary eye
tumors, such as malignant melanomas, can trigger a
subsequent orbital inflammatory response. 7
Inflammatory elements can present in both primary and
metastatic tumors within the orbit, with rhabdomyosarcoma
notably exhibiting features resembling an inflammatory
disorder. Patients with IDO should undergo thorough
evaluation for secondary infectious disorders stemming
from bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, as these
infections can precipitate severe inflammatory diseases. 8
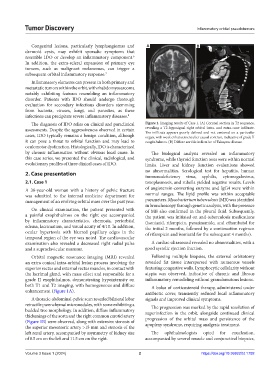
The diagnosis of IDO relies on clinical and paraclinical Figure 1. Imaging results of Case 1. (A) Coronal section in T2 sequence,
assessments. Despite the aggressiveness observed in certain revealing a T2-hyposignal right orbital intra- and extra-cone infiltrate.
The infiltrate appears poorly defined and not centered on a particular
cases, IDO typically remains a benign condition, although organ, with weak enhancement after causal contrast, indicative of grade II
it can pose a threat to orbital function and may lead to exophthalmos. (B) Diffuse aortitis indicative of Takayasu disease.
oculomotor dysfunction. Histologically, IDO is characterized
by chronic inflammation without obvious local cause. In The biological analysis revealed an inflammatory
this case series, we presented the clinical, radiological, and syndrome, while thyroid function tests were within normal
evolutionary profiles of three clinical cases of IDO. limits. Liver and kidney function evaluations showed
2. Case presentation no abnormalities. Serological test for hepatitis, human
immunodeficiency virus, syphilis, cytomegalovirus,
2.1. Case 1 toxoplasmosis, and rubella yielded negative results. Levels
A 38-year-old woman with a history of pelvic fracture of angiotensin-converting enzyme and IgG4 were within
was admitted to the internal medicine department for normal ranges. The lipid profile was within acceptable
management of an evolving orbital mass over the past year. parameters. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MB) was identified
in bronchoscopy through genetic analysis, with the presence
On clinical examination, the patient presented with of MB also confirmed in the pleural fluid. Subsequently,
a painful exophthalmos on the right eye accompanied the patient was initiated on anti-tuberculosis medications
by inflammatory characteristics, chemosis, periorbital (isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for
edema, lacrimation, and visual acuity of 4/10. In addition, the initial 2 months, followed by a continuation regimen
ocular hypertonia with blurred papillary edges in the of rifampicin and isoniazid for the subsequent 4 months).
temporal region of the eye was noted. The cardiovascular
examination also revealed a decreased right radial pulse A cardiac ultrasound revealed no abnormalities, with a
and a supraclavicular murmur. good systolic ejection fraction.
Orbital magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed Following multiple biopsies, the external orbitotomy
an extra conical intra-orbital lesion process involving the revealed fat tissue interspersed with numerous vessels
superior rectus and external rectus muscles, in contact with featuring congestive walls. Lymphocytic cellularity without
the lacrimal gland, with mass effect and responsible for a atypia was observed, indicative of chronic and fibrous
grade II exophthalmos, demonstrating hypointensity on inflammatory remodeling without granulomatous lesions.
both T1 and T2 imaging, with homogeneous and diffuse A bolus of corticosteroid therapy, administered under
enhancement (Figure 1A). antibiotic cover, transiently reduced local inflammatory
A thoracic-abdominal-pelvic scan revealed bilateral lobar signals and improved clinical symptoms.
retractile parenchymal micronodules, with some exhibiting a The progression was marked by the rapid resolution of
budded tree morphology. In addition, diffuse inflammatory superinfection in the orbit, alongside continued clinical
thickenings of the aorta and the right common carotid artery progression of the orbital mass and persistence of the
(Figure 1B) were observed, along with extensive stenosis of apoplexy syndrome, requiring analgesic treatment.
the superior mesenteric artery >15 mm and stenosis of the
left renal artery, accompanied by asymmetry of kidney size The ophthalmologists opted for enucleation,
of 8.5 cm on the left and 11.5 cm on the right. accompanied by several muscle and conjunctival biopsies,
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.1792