Page 118 - TD-3-1
P. 118
Tumor Discovery Inflammatory orbital pseudotumors
due to the unique characteristics of the intraorbital A B
tumor, which exhibited a solid and adherent consistency
reminiscent of cartilage. The sole concern was to eliminate
an underlying neoplastic process.
The final histological examination confirmed the
pseudotumor nature of the inflammatory process. It
revealed the presence of lymphoid cells and scattered
T-phenotype cells expressing CD3 alongside CD20
expression by numerous well-defined nodules lacking
expansive characteristics. In addition, a KI-67 proliferation
index of 10% was noted, particularly accentuated in the clear
germinal centers, along with vascular lesions. Furthermore, C
polyclonal rearrangement of the heavy and light kappa
chains of immunoglobulins was observed, definitively
ruling out the hypothesis of hemopathy or a solid tumor.
It was concluded that the patient had Takayasu disease,
as evidenced by a pseudo-orbital tumor in conjunction with
pulmonary tuberculosis. The diagnosis was based on the
fulfillment of four diagnostic criteria: age, decreased right
brachial pulse, supraclavicular murmur, and radiological
lesions consistent with diffuse thickenings of the aorta and D E
common carotid artery, as well as stenosis of the superior
mesenteric and left renal arteries. Following successful
anti-tuberculosis treatment, the patient was commenced
on infliximab therapy. Subsequently, there was a resolution
of clinical complaints and normalization of inflammatory
signals after 1 month of treatment. At the 6-month
follow-up, a positron emission tomography (PET) scan
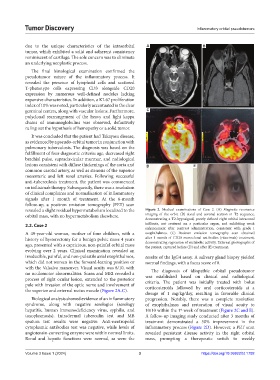
revealed a slight residual hypermetabolism localized to the Figure 2. Medical examinations of Case 2. (A) Magnetic resonance
orbital mass, with no hypermetabolism elsewhere. imaging of the orbit. (B) Axial and coronal section in T2 sequence,
demonstrating a T2-hyposignal, poorly defined right orbital intraconal
2.2. Case 2 infiltrate, not centered on a particular organ, and exhibiting weak
enhancement after contrast administration, consistent with grade I
A 49-year-old woman, mother of four children, with a exophthalmos. (C) Positron emission tomography scan obtained
history of hysterectomy for a benign pelvic mass 4 years after 1 month of CD20 monoclonal antibodies (rituximab) treatment,
ago, presented with a capricious, non-painful orbital mass demonstrating regression of metabolic activity. External photographs of
the patient, captured before (D) and after (E) treatment.
evolving over 2 years. Clinical examination revealed an
irreducible, painful, and non-pulsatile axial exophthalmos, results of the IgG4 assay. A salivary gland biopsy yielded
which did not worsen in the forward-leaning position or normal findings, with a focus score of 0.
with the Valsalva maneuver. Visual acuity was 8/10, with
no oculomotor abnormalities. Scans and MRI revealed a The diagnosis of idiopathic orbital pseudotumor
process of right ocular lesion, extended to the posterior was established based on clinical and radiological
criteria. The patient was initially treated with bolus
pole with invasion of the optic nerve and involvement of corticosteroids followed by oral corticosteroids at a
the superior and external rectus muscle (Figure 2A-C).
dosage of 1 mg/kg/day, resulting in favorable clinical
Biological analysis showed evidence of an inflammatory progression. Notably, there was a complete resolution
syndrome, along with negative serologies (serology of exophthalmos and restoration of visual acuity to
hepatitis, human immunodeficiency virus, syphilis, and 10/10 within the 1 week of treatment (Figure 2C and E).
st
toxoplasmosis). Intradermal tuberculin test and MB A follow-up imaging study conducted after 3 months of
sputum test results were negative. Anti-neutropohil treatment demonstrated a 50% improvement in the
cytoplasmic antibodies test was negative, while levels of inflammatory process (Figure 2D). However, a PET scan
angiotensin-converting enzyme were within normal limits. revealed persistent disease activity in the right orbital
Renal and hepatic functions were normal, as were the mass, prompting a therapeutic switch to weekly
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.1792