Page 16 - TD-3-3
P. 16
Tumor Discovery Immune and epigenetic therapies for TNBC
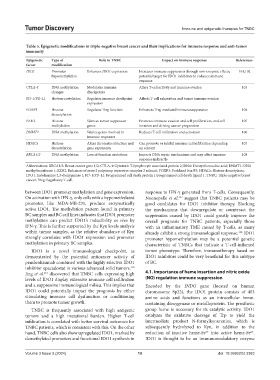
Table 5. Epigenetic modifications in triple‑negative breast cancer and their implications for immune response and anti‑tumor
immunity
Epigenetic Type of Role in TNBC Impact on immune response References
factor modification
IDO1 Promoter Enhances IDO1 expression Increases immune suppression through non-enzymic effects; 101,102
hypomethylation potential target for IDO1 inhibitors to enhance immune
response
CTLA-4 DNA methylation Modulates immune Alters T-cell activity and immune evasion 103
changes checkpoints
PD-1/PD-L1 Histone acetylation Regulates immune checkpoint Affects T-cell exhaustion and tumor immune evasion
expression
FOXP3 Histone Regulates Treg function Enhances Treg-mediated immunosuppression 104
deacetylation
EZH2 Histone Silences tumor suppressor Promotes immune evasion and cell proliferation, and cell 105
methylation genes invasion and driving cancer progression
DNMT1 DNA methylation Silence genes involved in Reduces T-cell infiltration and activation 106
immune responses
HDACs Histone Alters chromatin structure and Can promote or inhibit immune cell infiltration depending 107
deacetylation gene expression on context
BRCA1/2 DNA methylation Loss of function mutations Impacts DNA repair mechanisms and may affect immune 108
response indirectly
Abbreviations: BRCA1/2: Breast cancer gene 1/2; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 2; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; DNMT1: DNA
methyltransferase 1; EZH2: Enhancer of zeste 2 polycomp repressive complex 2 subunit; FOXP3: Forkhead box P3; HDACs: Histone deacetylases;
IDO1: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; PD-1/PD-L1: Programmed cell death protein 1/programmed cell death ligand 1; TNBC: Triple-negative breast
cancer; Treg: Regulatory T-cell.
between IDO1 promoter methylation and gene expression. response to IFN-γ generated from T-cells. Consequently,
On activation with IFN-γ, only cells with a hypomethylated Noonepalle et al. suggest that TNBC patients may be
117
promoter, like MDA-MB-231, produce enzymatically good candidates for IDO1 inhibitor therapy. Blocking
active IDO1. The methylation pattern found in primary the mechanisms that downregulate or counteract the
BC samples and BC cell lines indicates that IDO1 promoter suppression caused by IDO1 could greatly improve the
methylation can predict IDO1’s inducibility in vivo by overall prognosis for TNBC patients, especially those
IFN-γ. This is further supported by the Kyn levels analysis with an inflammatory TME caused by T-cells, as many
within tumor samples, as the relative abundance of Kyn already exhibit a strong immunological response. IDO1
118
strongly correlates with IDO1 expression and promoter promoter hypomethylation may be a potential genetic
methylation in primary BC samples. characteristic of TNBCs that indicate a T-cell-inflamed
IDO1 is a novel immunological checkpoint, as tumor phenotype. Therefore, immunotherapy based on
demonstrated by the potential anticancer activity of IDO1 inhibitors could be very beneficial for this subtype
pembrolizumab combined with the highly selective IDO1 of BC.
inhibitor epacadostat in various advanced solid tumors.
113
Jing et al. discovered that TNBC cells expressing high 4.1. Importance of heme insertion and nitric oxide
113
levels of IDO1 display extensive immune cell infiltration (NO) regulation immune suppression
and a suppressive immunological milieu. This implies that Encoded by the INDO gene (located on human
IDO1 could potentially impact the prognosis by either chromosome 8p22), the IDO1 protein consists of 403
stimulating immune cell dysfunction or conditioning amino acids and functions as an intracellular heme-
them to promote tumor growth. containing dioxygenase or metalloprotein. The prosthetic
TNBC is frequently associated with high antigenic group heme is necessary for its catalytic activity. IDO1
tumors and a high mutational burden. Higher T-cell catalyzes the oxidative cleavage of Trp to yield the
infiltration is correlated with better survival outcomes for intermediate product N-formylkynurenine, which is
TNBC patients, which is consistent with this. On the other subsequently hydrolyzed to Kyn, in addition to the
3+
2+
hand, TNBC cells also show upregulated IDO1, marked by reduction of inactive heme-Fe into active heme-Fe .
demethylated promoters and functional IDO1 synthesis in IDO1 is thought to be an immunomodulatory enzyme
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 10 doi: 10.36922/td.3383