Page 24 - TD-4-1
P. 24
Tumor Discovery Immunohistochemistry profiling of ovarian cysts
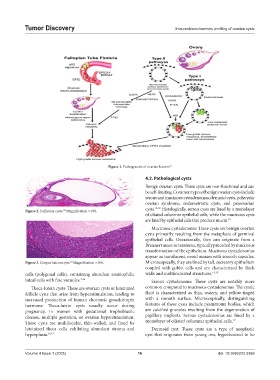
Figure 1. Pathogenesis of ovarian lesions 13
4.2. Pathological cysts
Benign ovarian cysts: These cysts are non-functional and can
be self-limiting. Common types of benign ovarian cysts include
serous and mucinous cystadenomas, dermoid cysts, polycystic
ovarian syndrome, endometriotic cysts, and paraovarian
cysts. 14,18 Histologically, serous cysts are lined by a monolayer
Figure 2. Follicular cysts. Magnification ×100.
23
of ciliated columnar epithelial cells, while the mucinous cysts
are lined by epithelial cells that produce mucin. 19
Mucinous cystadenoma: These cysts are benign ovarian
cysts primarily resulting from the metaplasia of germinal
epithelial cells. Occasionally, they can originate from a
Brenner tumor or teratoma, typically preceded by mucinous
transformation of the epithelium. Mucinous cystadenomas
appear as translucent, ovoid masses with smooth capsules.
Figure 3. Corpus luteum cyst. Magnification ×100. Microscopically, they are lined by tall, secretory epithelium
23
coupled with goblet cells and are characterized by thick
cells (polygonal cells), containing abundant eosinophilic walls and multiloculated structures. 14,19
luteal cells with fine vacuoles. 3,16 Serous cystadenoma: These cysts are notably more
Theca-lutein cysts: These are ovarian cysts or luteinized common compared to mucinous cystadenomas. The cystic
follicle cysts that arise from hyperstimulation, leading to fluid is characterized as thin, watery, and yellow-tinged
increased production of human chorionic gonadotropin with a smooth surface. Microscopically, distinguishing
hormone. Theca-lutein cysts usually occur during features of these cysts include psammoma bodies, which
pregnancy, in women with gestational trophoblastic are calcified granules resulting from the degeneration of
disease, multiple gestation, or ovarian hyperstimulation. papillary implants. Serous cystadenomas are lined by a
These cysts are multilocular, thin-walled, and lined by monolayer of ciliated columnar epithelial cells. 19
luteinized theca cells exhibiting abundant stroma and Dermoid cyst: These cysts are a type of neoplastic
hyperplasia. 16,17 cyst that originates from young ova, hypothesized to be
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 16 doi: 10.36922/td.5369