Page 101 - TD-4-3
P. 101
Tumor Discovery Complete response to enfortumab vedotin in mBC
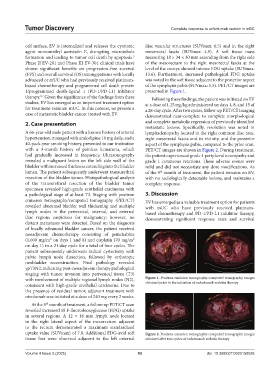
cell surface, EV is internalized and releases the cytotoxic iliac vascular structures (SUVmax: 6.5) and in the right
agent monomethyl auristatin E, disrupting microtubule mesorectal fascia (SUVmax: 4.9). A soft tissue mass
formation and leading to tumor cell death by apoptosis. measuring 18 × 34 × 30 mm extending from the right side
5
Phase II EV-201 and Phase III EV-301 clinical trials have of the mesorectum to the right mesorectal fascia at the
shown significant benefits on progression-free survival level of the coccyx showed intense FDG uptake (SUVmax:
(PFS) and overall survival (OS) among patients with locally 13.6). Furthermore, increased pathological FDG uptake
advanced or mUC who had previously received platinum- was noted in the soft tissue adjacent to the posterior aspect
based chemotherapy and programmed cell death protein of the symphysis pubis (SUVmax: 5.5). PET/CT images are
1/programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitor presented in Figure 1.
therapy. Given the significance of the findings from these Following these findings, the patient was initiated on EV
6,7
studies, EV has emerged as an important treatment option at a dose of 1.25 mg/kg administered on days 1, 8, and 15 of
for treatment-resistant mUC. In this context, we present a a 28-day cycle. After two cycles, follow-up PET/CT imaging
case of metastatic bladder cancer treated with EV. demonstrated near-complete to complete morphological
2. Case presentation and complete metabolic regression of previously identified
metastatic lesions. Specifically, resolution was noted in
A 66-year-old male patient with a known history of arterial lymphadenopathy located in the right common iliac area,
hypertension, managed with amlodipine 10 mg daily, and a right mesorectal fascia and its vicinity, and the posterior
40-pack-year smoking history, presented to our institution aspect of the symphysis pubis, compared to the prior scan.
with a 3-month history of painless hematuria, which PET/CT images are shown in Figure 2. During treatment,
had gradually increased in frequency. Ultrasonography the patient experienced grade 1 peripheral neuropathy and
revealed a malignant lesion on the left side wall of the grade 1 cutaneous reactions. These adverse events were
bladder with increased thickness extending into the bladder mild and did not necessitate any dose modifications. As
lumen. The patient subsequently underwent transurethral of the 9 month of treatment, the patient remains on EV,
th
resection of the bladder tumor. Histopathological analysis with no radiologically detectable lesions, and maintains a
of the transurethral resection of the bladder tumor complete response.
specimen revealed high-grade urothelial carcinoma with
a pathological stage of at least T2. Staging with positron 3. Discussion
emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) EV has emerged as a valuable treatment option for patients
revealed abnormal bladder wall thickening and multiple with mUC who have previously received platinum-
lymph nodes in the perivesical, internal, and external based chemotherapy and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor therapy,
iliac regions suspicious for malignancy; however, no demonstrating significant response rates and survival
distant metastases were detected. Based on the diagnosis
of locally advanced bladder cancer, the patient received
neoadjuvant chemotherapy consisting of gemcitabine
(1,000 mg/m² on days 1 and 8) and cisplatin (70 mg/m²
on day 1) in a 21-day cycle for a total of four cycles. The
patient subsequently underwent radical cystectomy with
pelvic lymph node dissection, followed by orthotopic
neobladder reconstruction. Final pathology revealed
ypT3N2, indicating post-neoadjuvant therapy pathological
staging with tumor invasion into perivesical tissue (T3)
with involvement of multiple regional lymph nodes (N2), Figure 1. Positron emission tomography-computed tomography images
consistent with high-grade urothelial carcinoma. Due to obtained prior to the initiation of enfortumab vedotin therapy
the presence of residual tumor, adjuvant treatment with
nivolumab was initiated at a dose of 240 mg every 2 weeks.
At the 9 month of treatment, a follow-up PET/CT scan
th
revealed increased 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake
in several regions. A 12 × 16 mm lymph node located
in the right lateral aspect of the mesorectum adjacent
to the rectum demonstrated a maximum standardized
uptake value (SUVmax) of 7.8. Additional FDG-avid soft Figure 2. Positron emission tomography-computed tomography images
tissue foci were observed adjacent to the left external obtained after two cycles of enfortumab vedotin therapy
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 93 doi: 10.36922/TD025150026