Page 27 - TD-4-3
P. 27
Tumor Discovery Immunomodulatory effects of CDK4/6 inhibitors
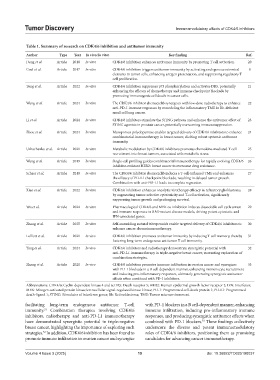
Table 1. Summary of research on CDK4/6 inhibition and antitumor immunity
Author Type Year In vivo/In vitro Key finding Ref.
Deng et al. Article 2018 In vitro CDK4/6 inhibition enhances antitumor immunity by promoting T cell activation. 20
Goel et al. Article 2017 In vitro CDK4/6 inhibition triggers antitumor immunity by activating endogenous retroviral 8
elements in tumor cells, enhancing antigen presentation, and suppressing regulatory T
cell proliferation.
Tong et al. Article 2022 In vitro CDK4/6 inhibition suppresses p73 phosphorylation and activates DR5, potentially 21
enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade by
promoting immunogenic cell death in cancer cells.
Wang et al. Article 2024 In vitro The CDK4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib synergizes with low-dose radiotherapy to enhance 22
anti-PD-1 immune responses by remodeling the inflammatory TME in Rb-deficient
small cell lung cancer.
Li et al. Article 2024 In vitro CDK4/6 inhibitors stimulate the STING pathway and enhance the antitumor effect of 23
STING agonists in prostate cancer, potentially overcoming immunosuppression.
Zhou et al. Article 2024 In vitro Mesoporous polydopamine enables targeted delivery of CDK4/6 inhibitors to enhance 24
combinatorial immunotherapy in breast cancer, eliciting robust systemic antitumor
immunity.
Uzhachenko et al. Article 2021 In vitro Metabolic modulation by CDK4/6 inhibitors promotes chemokine-mediated T cell 25
recruitment into breast tumors, associated with metabolic stress.
Wang et al. Article 2019 In vitro Single-cell profiling guides combinatorial immunotherapy for rapidly evolving CDK4/6 26
inhibitor-resistant HER2+breast cancer to overcome drug resistance.
Schaer et al. Article 2018 In vitro The CDK4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib induces a T-cell-inflamed TME and enhances 27
the efficacy of PD-L1 checkpoint blockade, resulting in delayed tumor growth.
Combination with anti-PD-L1 leads to complete regression.
Xiao et al. Article 2022 In vitro CDK4/6 inhibition enhances oncolytic virotherapy efficacy in refractory glioblastoma 28
by augmenting tumor-selective cytotoxicity and T-cell activation, significantly
suppressing tumor growth and prolonging survival.
Wu et al. Article 2024 In vitro Pharmacological CDK4/6 and MEK co-inhibition induces dissociable cell cycle arrest 29
and immune responses in RAS-mutant disease models, driving potent cytostatic and
IFN-associated genes.
Zhang et al. Article 2025 In vitro Self-assembling natural triterpenoids enable targeted delivery of CDK4/6 inhibitors to 30
enhance cancer chemoimmunotherapy.
Lelliott et al. Article 2021 In vivo CDK4/6 inhibition promotes antitumor immunity by inducing T cell memory, thereby 31
fostering long-term endogenous antitumor T cell immunity.
Yang et al. Article 2024 In vivo CDK4/6 inhibitors and radiotherapy demonstrate synergistic potential with 32
anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer, warranting exploration of
combination strategies.
Zhang et al. Article 2020 In vivo CDK4/6 inhibition promotes immune infiltration in ovarian cancer and synergizes 33
with PD-1 blockade in a B cell-dependent manner, enhancing immunocyte recruitment
and inducing pro-inflammatory responses, ultimately generating synergistic antitumor
effects when combined with PD-1 inhibitors.
Abbreviations: CDK4/6: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6; DR5: Death receptor 5; HER2: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IFN: Interferon;
MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1: Programmed
death-ligand 1; STING: Stimulator of interferon genes; Rb: Retinoblastoma; TME: Tumor microenvironment.
facilitating long-term endogenous antitumor T-cell with PD-1 blockers in a B cell-dependent manner, enhancing
immunity. Combination therapies involving CDK4/6 immune infiltration, inducing pro-inflammatory immune
31
inhibitors, radiotherapy, and anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy responses, and producing synergistic antitumor effects when
have demonstrated synergistic potential in triple-negative combined with PD-1 blockers. These findings collectively
33
breast cancer, highlighting the importance of exploring such underscore the diverse and potent immunomodulatory
strategies. In addition, CDK4/6 inhibition has been found to roles of CDK4/6 inhibitors, positioning them as promising
32
promote immune infiltration in ovarian cancer and synergize candidates for advancing cancer immunotherapy.
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 19 doi: 10.36922/TD025190037