Page 28 - TD-4-3
P. 28
Tumor Discovery Immunomodulatory effects of CDK4/6 inhibitors
5. Mechanisms of immunomodulatory upregulation of max dimerization protein 4 (MXD4), a
effects of CDK4/6 inhibitors negative regulator of myelocytomatosis viral oncogene
homolog (MYC) in CD8 T cells, thereby sustaining durable
+
5.1. Enhancement of immune cell responses antitumor immunity. 31,34 In breast cancer patients, palbociclib
+
5.1.1. T-cell responses or abemaciclib treatment increases the proportion of CD8 T
memory precursor cells while suppressing MYC target gene
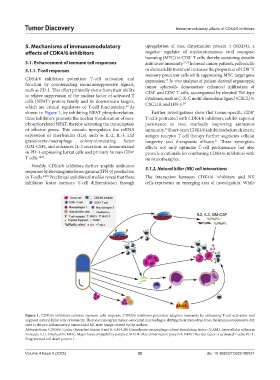
CDK4/6 inhibitors potentiate T-cell activation and expression. In vivo analyses of patient-derived organotypic
34
function by counteracting immunosuppressive signals, tumor spheroids demonstrate enhanced infiltration of
such as PD-1. This effect primarily stems from their ability CD4 and CD8 T cells, accompanied by elevated Th1-type
+
+
to relieve suppression of the nuclear factor of activated T cytokines, such as C-X-C motif chemokine ligand (CXCL) 9,
cells (NFAT) protein family and its downstream targets, CXCL10, and IFN-γ. 20
20
which are critical regulators of T-cell functionality. As
+
shown in Figure 1, by inhibiting NFAT phosphorylation, Further investigations show that tumor-specific CD8
these inhibitors promote the nuclear translocation of non- T cells pretreated with CDK4/6 inhibitors exhibit superior
phosphorylated NFAT, thereby activating the transcription persistence in vivo, markedly improving antitumor
of effector genes. This cascade upregulates the mRNA immunity. Short-term CDK4/6 inhibition before chimeric
34
expression of interleukins (ILs), such as IL-2, IL-3, and antigen receptor T cell therapy further augments cellular
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor longevity and therapeutic efficacy. These synergistic
31
(GM-CSF), and enhances IL-2 secretion, as demonstrated effects not only optimize T-cell performance but also
+
in PD-1-expressing Jurkat cells and primary human CD4 provide a rationale for combining CDK4/6 inhibitors with
T cells. 34,35 immunotherapies.
Notably, CDK4/6 inhibitors further amplify antitumor
responses by elevating interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) production 5.1.2. Natural killer (NK) cell interactions
in T-cells. 34,35 Preclinical and clinical studies reveal that these The interaction between CDK4/6 inhibitors and NK
inhibitors foster memory T-cell differentiation through cells represents an emerging area of investigation. While
Figure 1. CDK4/6 inhibitors enhance immune cells response. CDK4/6 inhibitors potentiate adaptive immunity by enhancing T-cell activation and
augment natural killer cells cytotoxicity. They also reprogram tumor-associated macrophages, shifting their phenotype from the immunosuppressive M2
state to the pro-inflammatory, tumoricidal M1 state. Image created by the authors.
Abbreviations: CDK4/6: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ICAM1: Intercellular adhesion
molecule 1; IL: Interleukin; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; MXD4: Max dimerization protein 4; NFAT: Nuclear factor of activated T cells; PD-1:
Programmed cell death protein 1.
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 20 doi: 10.36922/TD025190037