Page 23 - manuscript_ijb05580
P. 23
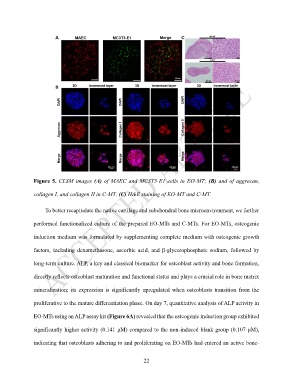
Figure 5. CLSM images (A) of MAEC and MC3T3-E1 cells in EO-MT; (B) and of aggrecan,
collagen I, and collagen II in C-MT. (C) H&E staining of EO-MT and C-MT.
To better recapitulate the native cartilage and subchondral bone microenvironment, we further
performed functionalized culture of the prepared EO-MTs and C-MTs. For EO-MTs, osteogenic
induction medium was formulated by supplementing complete medium with osteogenic growth
factors, including dexamethasone, ascorbic acid, and β-glycerophosphate sodium, followed by
long-term culture. ALP, a key and classical biomarker for osteoblast activity and bone formation,
directly reflects osteoblast maturation and functional status and plays a crucial role in bone matrix
mineralization; its expression is significantly upregulated when osteoblasts transition from the
proliferative to the mature differentiation phase. On day 7, quantitative analysis of ALP activity in
EO-MTs using an ALP assay kit (Figure 6A) revealed that the osteogenic induction group exhibited
significantly higher activity (0.141 μM) compared to the non-induced blank group (0.107 μM),
indicating that osteoblasts adhering to and proliferating on EO-MTs had entered an active bone-
22