Page 31 - AIH-1-2
P. 31
Artificial Intelligence in Health LLMs-Healthcare: Application and challenges
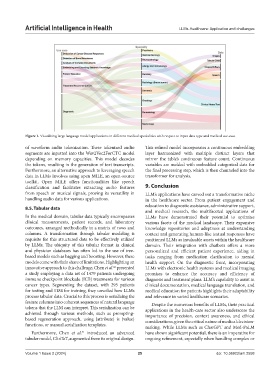
Figure 1. Visualizing large language model applications in different medical specialities with respect to input data type and medical use-case.
of waveform audio tokenization. These tokenized audio This refined model incorporates a continuous embedding
segments are inputted into the Wav2Vec2ForCTC model layer harmonized with multiple distinct layers that
depending on memory capacities. This model decodes mirror the table’s continuous feature count. Continuous
the tokens, resulting in the generation of text transcripts. variables are melded with embedded categorical data for
Furthermore, an alternative approach to leveraging speech the final processing step, which is then channeled into the
data in LLMs involves using open MILE, an open-source transformer for analysis.
toolkit. Open MILE offers functionalities like speech
classification and facilitates extracting audio features 9. Conclusion
from speech or musical signals, proving its versatility in LLM’s applications have carved out a transformative niche
handling audio data for various applications. in the healthcare sector. From patient engagement and
education to diagnostic assistance, administrative support,
8.5. Tabular data
and medical research, the multifaceted applications of
In the medical domain, tabular data typically encompasses LLMs have demonstrated their potential to optimize
clinical measurements, patient records, and laboratory various facets of the medical landscape. Their expansive
outcomes, arranged methodically in a matrix of rows and knowledge repositories and adeptness at understanding
columns. A transformation through tabular modeling is context and generating human-like textual responses have
requisite for this structured data to be effectively utilized positioned LLMs as invaluable assets within the healthcare
by LLMs. The ubiquity of this tabular format in clinical domain. Their integration with chatbots offers a more
and physician databases has often led to the use of tree- personalized and efficient patient experience, aiding in
based models such as bagging and boosting. However, these tasks ranging from medication clarification to mental
models come with their share of limitations. Highlighting an health support. On the diagnostic front, incorporating
innovative approach to this challenge, Chen et al. presented LLMs with electronic health systems and medical imaging
41
a study employing a data set of 1479 patients undergoing promises to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of
immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) treatments for various diagnosis and treatment plans. LLM’s capability to assist in
cancer types. Segmenting the dataset, with 295 patients clinical documentation, medical language translation, and
for testing and 1184 for training, they unveiled how LLMs medical education for patients highlights their adaptability
process tabular data. Crucial to this process is serializing the and relevance in varied healthcare scenarios.
feature columns into coherent sequences of natural language Despite the numerous benefits of LLMs, their practical
tokens that the LLM can interpret. This serialization can be applications in the health-care sector also underscore the
achieved through various methods, such as prompting- importance of precision, context awareness, and ethical
based regeneration approach, using {attribute} is {value} considerations, given the critical nature of medical decision-
functions, or manual serialization templates. making. While LLMs such as ChatGPT and Med-PaLM
Furthermore, Chen et al. introduced an advanced have shown significant potential, there is an imperative for
41
tabular model, ClinTaT, augmented from its original design. ongoing refinement, especially when handling complex or
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 25 doi: 10.36922/aih.2558