Page 56 - AIH-1-2
P. 56
Artificial Intelligence in Health AI in AD – Diagnosis and monitoring
A B
C
D
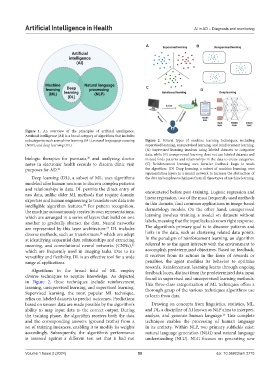
Figure 1. An overview of the principles of artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad category of algorithms that includes
subcategories such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing Figure 2. Several types of machine learning techniques, including
(NLP), and deep learning (DL). supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
(A) Supervised learning involves using labeled datasets to categorize
data, while (B) unsupervised learning does not use labeled datasets and
biologic therapies for psoriasis, and analyzing doctor instead finds patterns and relationships in the data to create categories.
20
notes in electronic health records to discern clinic visit (C) Reinforcement learning uses iterative feedback loops to teach
purposes for AD. 21 the algorithm. (D) Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, uses
representation layers in a neural network to increase the abstraction of
Deep learning (DL), a subset of ML, uses algorithms the data and employs techniques from all three types of machine learning.
modeled after human neurons to discern complex patterns
and relationships in data. DL permits the direct entry of encountered before post-training. Logistic regression and
raw data, unlike older ML methods that require domain linear regression, two of the most frequently used methods
expertise and human engineering to translate raw data into
intelligible algorithm features. For pattern recognition, in this domain, find common applications in image-based
22
the machine autonomously creates its own representations, dermatology models. On the other hand, unsupervised
which are arranged in a series of layers that build on one learning involves training a model on datasets without
another to gradually abstract the data. Neural networks labels, meaning that the input lacks a known right response.
are represented by this layer architecture. DL includes The algorithm’s primary goal is to discover patterns and
23
diverse methods, such as transformers, which are adept links in the data, such as clustering related data points.
24
at identifying sequential data relationships and extracting In the paradigm of reinforcement learning, an algorithm
meaning, and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), referred to as the agent interacts with the environment to
25
which are frequently used in imaging tasks. Due to its accomplish predetermined objectives. Based on feedback,
versatility and flexibility, DL is an effective tool for a wide it receives from its actions in the form of rewards or
range of applications. penalties, the agent modifies its behavior to optimize
rewards. Reinforcement learning learns through ongoing
Algorithms in the broad field of ML employ feedback loops, distinct from the predetermined data input
diverse techniques to acquire knowledge. As depicted found in supervised and unsupervised learning methods.
in Figure 2, these techniques include reinforcement This three-class categorization of ML techniques offers a
learning, unsupervised learning, and supervised learning. thorough grasp of the various techniques algorithms use
Supervised learning, the most popular ML technique, to learn from data.
relies on labeled datasets to predict outcomes. Predictions
based on unseen data are made possible by the algorithm’s Drawing on concepts from linguistics, statistics, ML,
ability to map input data to the correct output. During and DL, a discipline of AI known as NLP aims to interpret,
the training phase, the algorithm receives both the data analyze, and generate human language. This complete
26
and the corresponding answers (ground truths) from a technique enables the processing of human language
set of training instances, enabling it to modify its weights in its entirety. Within NLP, two primary subfields exist:
accordingly. Subsequently, the algorithm’s performance natural language generation (NLG) and natural language
is assessed against a different test set that it had not understanding (NLU). NLG focuses on generating new
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 50 doi: 10.36922/aih.2775