Page 59 - AIH-1-2
P. 59
Artificial Intelligence in Health AI in AD – Diagnosis and monitoring
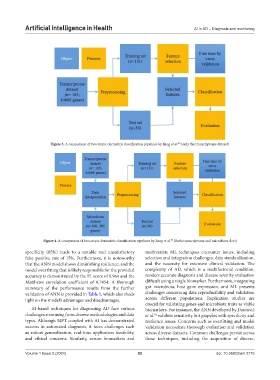
Figure 3. A comparison of two atopic dermatitis classification pipelines by Jiang et al. (only the transcriptome dataset)
50
Figure 4. A comparison of two atopic dermatitis classification pipelines by Jiang et al. (Both transcriptome and microbiota data)
50
specificity (85%) leads to a notable and unsatisfactory multivariate ML techniques encounter issues, including
false positive rate of 15%. Furthermore, it is noteworthy selection and integration challenges, data standardization,
that the ANN model shows diminishing resilience, and the and the necessity for extensive clinical validation. The
model over fitting that is likely responsible for the provided complexity of AD, which is a multifactorial condition,
accuracy is demonstrated by the F1 score of 0.964 and the renders accurate diagnosis and disease severity evaluation
Matthews correlation coefficient of 0.7454. A thorough difficult using a single biomarker. Furthermore, integrating
summary of the performance results from the further gut microbiota, host gene expression, and ML presents
validation of ANN is provided in Table 1, which also sheds challenges concerning data reproducibility and validation
light on the model’s advantages and disadvantages. across different populations. Replication studies are
crucial for validating genes and microbiota traits as viable
AI-based techniques for diagnosing AD face various biomarkers. For instance, the ANN developed by Dautović
challenges stemming from diverse methodologies and data et al. exhibits sensitivity but grapples with specificity and
51
types. Although MPT coupled with AI has demonstrated resilience issues. Concerns such as overfitting and model
success in automated diagnosis, it faces challenges such validation necessitate thorough evaluation and validation
as robust generalization, real-time application feasibility, across diverse datasets. Common challenges persist across
and ethical concerns. Similarly, serum biomarkers and these techniques, including the acquisition of diverse,
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 53 doi: 10.36922/aih.2775