Page 89 - AIH-2-1
P. 89
Artificial Intelligence in Health Benchmarking ML imputation in mental health surveys
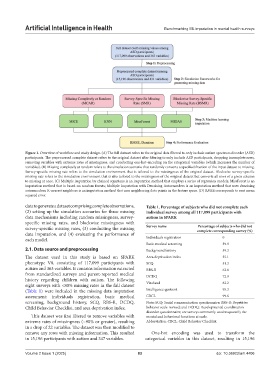
Figure 1. Overview of workflow and study design. (A) The full dataset refers to the original data filtered to only include autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
participants. The preprocessed complete dataset refers to the original dataset after filtering to only include ASD participants, dropping incomplete rows,
removing variables with extreme rates of missingness, and conducting one-hot-encoding on the categorical variables (which increases the number of
variables). (B) Missing completely at random refers to the simulation scenario that randomly converts a specified fraction of the input dataset to missing.
Survey-specific missing rate refers to the simulation environment that is tailored to the missingness of the original dataset. Blockwise survey-specific
missing rate refers to the simulation environment that is also tailored to the missingness of the original dataset but converts all rows of a given column
to missing at once. (C) Multiple imputation by chained equations is an imputation method that employs a series of regression models; MissForest is an
imputation method that is based on random forests; Multiple Imputation with Denoising Autoencoders is an imputation method that uses denoising
autoencoders; K-nearest neighbors is an imputation method that uses neighboring data points in the feature space. (D) RMSE corresponds to root mean
squared error.
data to generate a dataset comprising complete observations, Table 1. Percentage of subjects who did not complete each
(2) setting up the simulation scenarios for three missing individual survey among all 117,099 participants with
data mechanisms including random missingness, survey- autism in SPARK
specific missing rates, and blockwise missingness with
Percentage of subjects who did not
survey-specific missing rates, (3) conducting the missing Survey name complete corresponding survey (%)
data imputation, and (4) evaluating the performance of
each model. Individuals registration 0
Basic medical screening 39.9
2.1. Data source and preprocessing Background history 59.3
The dataset used in this study is based on SPARK Area deprivation index 35.1
phenotype V8, consisting of 117,099 participants with SCQ 51.3
autism and 363 variables. It contains information extracted RBS-R 63.8
from standardized surveys and parent-reported medical DCDQ 72.9
history regarding children with autism. The following
eight surveys with <80% missing rates in the full dataset Vineland 82.2
(Table 1) were included in the missing data imputation Intelligence quotient 95.3
assessment: individuals registration, basic medical CBCL 99.6
screening, background history, SCQ, RBS-R, DCDQ, Note: SCQ: Social communication questionnaire; RBS-R: Repetitive
Child Behavior Checklist, and area deprivation index. behavior scale-revised; and DCDQ: Developmental coordination
disorder questionnaire; are surveys commonly used to quantify the
This dataset was first filtered to remove variables with mental and behavioral functions at scale.
extreme rates of missingness (~90% or greater), resulting Abbreviation: CBCL: Child Behavior Checklist.
in a drop of 22 variables. The dataset was then modified to
remove any rows with missing information. This resulted One-hot encoding was used to transform the
in 15,196 participants with autism and 347 variables. categorical variables in this dataset, resulting in 15,196
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 83 doi: 10.36922/aih.4406