Page 124 - AIH-2-4
P. 124
Artificial Intelligence in Health RefSAM3D for medical image segmentation
A
B C D
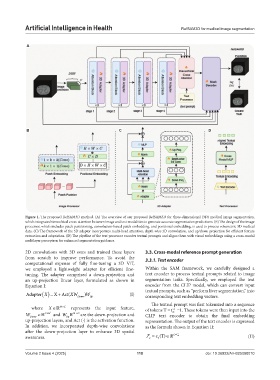
Figure 1. The proposed RefSAM3D method. (A) The overview of our proposed RefSAM3D for three-dimensional (3D) medical image segmentation,
which integrates hierarchical cross-attention between image and text modalities to generate accurate segmentation predictions. (B) The design of the image
processor, which includes patch partitioning, convolution-based patch embedding, and positional embedding, is used to process volumetric 3D medical
data. (C) The framework of the 3D adapter incorporates multi-head attention, depth-wise 3D convolution, and up/down projection for efficient feature
extraction and adaptation. (D) The pipeline of the text processor encodes textual prompts and aligns them with visual embeddings using a cross-modal
multilayer perceptron for enhanced segmentation guidance.
2D convolutions with 3D ones and trained these layers 3.3. Cross-modal reference prompt generation
from scratch to improve performance. To avoid the 3.3.1. Text encoder
computational expense of fully fine-tuning a 3D ViT,
we employed a lightweight adapter for efficient fine- Within the SAM framework, we carefully designed a
tuning. The adapter comprised a down-projection and text encoder to process textual prompts related to image
an up-projection linear layer, formulated as shown in segmentation tasks. Specifically, we employed the text
Equation I: encoder from the CLIP model, which can convert input
textual prompts, such as “perform liver segmentation,” into
Adapter X X Act XW ( Down ) W Up (I) corresponding text embedding vectors.
The textual prompt was first tokenized into a sequence
where X NC represents the input feature, of tokens T =t =1. These tokens were then input into the
L
ll
W Down CN ’ and W NC× ’ are the down-projection and CLIP text encoder to obtain the final embedding
Up
up-projection layers, and Act (·) is the activation function. representation. The output of the text encoder is expressed
In addition, we incorporated depth-wise convolutions as the formula shown in Equation II:
after the down-projection layer to enhance 3D spatial
awareness. ()T LC e (II)
e
t
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 118 doi: 10.36922/AIH025080010