Page 148 - AIH-2-4
P. 148
Artificial Intelligence in Health AI-driven personalized learning in residency
Table 1. Summary of descriptive statistics Table 2. Pearson correlation matrix of resident engagement
and quiz performance variables
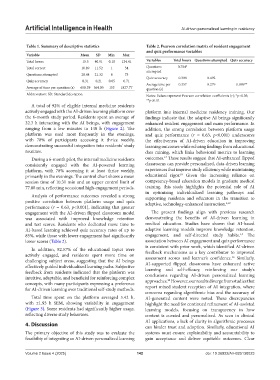
Variable Mean SD Min Max
Total hours 15.5 40.91 0.18 124.41 Variables Total hours Questions attempted Quiz accuracy
Total correct 10.89 11.52 1 34 Questions 0.784*
attempted
Questions attempted 28.44 21.32 6 73
Quiz accuracy 0.308 0.492
Quiz accuracy 0.31 0.21 0.05 0.71
Average time per 0.357 0.279 0.889**
Average of time per question (s) 658.39 564.05 153 1827.77 question (s)
Abbreviation: SD: Standard deviation. Notes: Values represent Pearson correlation coefficients (r); *p<0.05;
**p<0.01.
A total of 92% of eligible internal medicine residents
actively engaged with the AI-driven learning platform over platform into internal medicine residency training. Our
the 6-month study period. Residents spent an average of findings indicate that the adaptive AI beings significantly
32.3 h interacting with the AI beings, with engagement enhanced resident engagement and exam performance. In
ranging from a few minutes to 148 h (Figure 2). The addition, the strong correlation between platform usage
platform was used most frequently in the evenings, and quiz performance (r = 0.63, p<0.001) underscores
with 78% of participants accessing it thrice weekly, the effectiveness of AI-driven education in improving
demonstrating successful integration into residents’ study learning outcomes while echoing findings from educational
routines. data mining, which links behavioral metrics to learning
17
During a 6-month pilot, the internal medicine residents outcomes. These results suggest that AI-enhanced flipped
consistently engaged with the AI-powered learning classrooms can provide personalized, data-driven learning
platform, with 78% accessing it at least thrice weekly, experiences that improve study efficiency while maintaining
18
primarily in the evenings. The control chart shows a mean educational rigor. Given the increasing reliance on
session time of 10.31 min and an upper control limit of competency-based education models in graduate medical
77.08 min, reflecting occasional high-engagement periods. training, this study highlights the potential role of AI
in optimizing individualized learning pathways and
Analysis of performance outcomes revealed a strong
positive correlation between platform usage and quiz supporting residents and educators in the transition to
adaptive, technology-enhanced instruction.
2,19
performance (r = 0.63, p<0.001), indicating that greater
engagement with the AI-driven flipped classroom model The present findings align with previous research
was associated with improved knowledge retention demonstrating the benefits of AI-driven learning in
and test scores. Residents who dedicated more time to medical education. Studies have shown that AI-based
AI-based learning achieved quiz accuracy rates of up to adaptive learning models improve knowledge retention,
1,5
85%, while those with lower engagement had significantly engagement, and self-directed study habits. The
lower scores (Table 2). association between AI engagement and quiz performance
is consistent with prior work, which identified AI-driven
In addition, 82.57% of the educational topics were
actively engaged, and residents spent more time on feedback mechanisms as a key contributor to improved
13
challenging subject areas, suggesting that the AI beings assessment scores and learner’s confidence. Similarly,
AI-supported flipped classrooms have enhanced active
effectively guided individualized learning paths. Subjective learning and self-efficacy, reinforcing our study’s
feedback from residents indicated that the platform was conclusions regarding AI-driven personalized learning
intuitive, adaptable, and beneficial for reinforcing complex 20
concepts, with many participants expressing a preference approaches. However, our results diverge from studies that
for AI-driven learning over traditional self-study methods. report mixed student reception of AI integration, where
concerns regarding algorithmic bias and the accuracy of
Total time spent on the platform averaged 5.42 h, AI-generated content were noted. These discrepancies
with ±1.93 h SEM, showing variability in engagement highlight the need for continued refinement of AI-assisted
(Figure 3). Some residents had significantly higher usage, learning models, focusing on transparency in how
reflecting diverse study behaviors. content is curated and personalized. As seen in clinical
AI applications, a lack of clarity in algorithmic processes
4. Discussion can hinder trust and adoption. Similarly, educational AI
The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the systems must ensure explainability and accountability to
feasibility of integrating an AI-driven personalized learning gain acceptance and deliver equitable outcomes. Clear
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 142 doi: 10.36922/AIH025130023