Page 35 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 35
Heterogeneous catalysts for biodiesel production
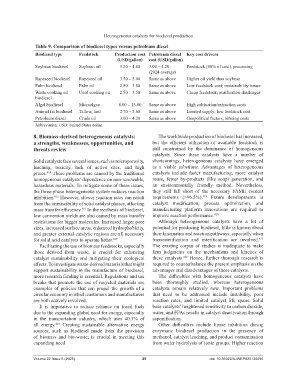
Table 9. Comparison of biodiesel types versus petroleum diesel
Biodiesel type Feedstock Production cost Petroleum diesel Key cost drivers
(USD/gallon) cost (USD/gallon)
Soybean biodiesel Soybean oil 3.20 – 4.80 3.00 – 4.20 Feedstock (80% of cost), processing
(2024 average)
Rapeseed biodiesel Rapeseed oil 3.50 – 5.00 Same as above Higher oil yield than soybean
Palm biodiesel Palm oil 2.80 – 3.80 Same as above Low feedstock cost; sustainability issues
Waste cooking oil Used cooking oil 2.50 – 3.50 Same as above Cheap feedstock; purification challenges
biodiesel
Algal biodiesel Microalgae 8.00 – 15.00 Same as above High cultivation/extraction costs
Animal fat biodiesel Tallow, lard 2.70 – 3.60 Same as above Limited supply; low feedstock cost
Petroleum diesel Crude oil 3.00 – 4.20 Same as above Geopolitical factors, refining costs
Abbreviation: USD: United States dollar.
8. Biomass-derived heterogeneous catalysts: The worldwide production of biodiesel has increased,
a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and but the efficient utilization of available feedstock is
threats review still constrained by the dominance of homogeneous
catalysts. Since these catalysts have a number of
Solid catalysts face several issues, such as microporosity, shortcomings, heterogeneous catalysts have emerged
leaching, toxicity, lack of active sites, and high as a viable substitute. Advantages of heterogeneous
prices. These problems are caused by the traditional catalysts include faster manufacturing, more catalyst
414
homogeneous catalysts’ dependence on non-renewable, reuse, fewer by-products (like soap) generation, and
hazardous materials. To mitigate some of these issues, an environmentally friendly method. Nevertheless,
the three-phase heterogeneous system reduces reaction they still fall short of the necessary FAME content
inhibition. However, slower reaction rates can result requirements (>96.5%). Future developments in
419
415
from the immiscibility of solid catalyst phases, affecting catalyst modification, process optimization, and
mass transfer efficiency. In the synthesis of biodiesel, manufacturing platform innovations are required to
416
low conversion yields are also caused by mass transfer improve reaction performance. 420
restrictions for bigger molecules. Increased larger pore Although heterogeneous catalysts have a lot of
sizes, increased surface areas, enhanced hydrophobicity, potential for producing biodiesel, little is known about
and greater external catalytic regions are all necessary their kinematics and reaction pathways, especially when
for solid acid catalysts to operate better. 417 transesterification and esterification are involved.
421
Facilitating the use of biomass feedstocks, especially The existing corpus of studies is inadequate to make
those derived from waste, is crucial for enhancing firm judgments on the mechanisms and kinetics of
catalyst sustainability and mitigating their ecological these catalysts. Hence, further thorough research is
422
effects. To investigate waste-derived materials that might required to counterbalance the present emphasis on the
support sustainability in the manufacture of biodiesel, advantages and disadvantages of these catalysts.
more research funding is essential. Regulations and tax The difficulties with homogeneous catalysts have
breaks that promote the use of recycled materials are been thoroughly studied, whereas heterogeneous
examples of policies that can propel the growth of a catalysts remain relatively new. Important problems
circular economy in which customers and manufacturers that need to be addressed include instability, poor
are both actively involved. reaction rates, and limited catalyst life spans. Solid
It is imperative to reduce reliance on fossil fuels base catalysts’ heightened sensitivity to carbon dioxide,
due to the expanding global need for energy, especially water, and FFAs results in catalyst deactivation through
in the transportation industry, which uses 40.5% of saponification.
all energy. Creating sustainable alternative energy Other difficulties include lipase inhibition during
418
sources, such as biodiesel made from the provision enzymatic biodiesel production in the presence of
of biomass and bio-waste, is crucial in meeting this methanol, catalyst leaching, and product contamination
expanding need. from water hydrolysis of ionic groups. Higher reaction
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 29 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025130095