Page 75 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 75
Hybrid optimization for LSTM DO prediction
the performance bottlenecks typically faced by a single
optimization algorithm. Experimental results also
confirm that this approach achieves faster convergence
speed and higher solution quality compared across
multiple benchmark function tests, demonstrating
its practical effectiveness for solving complex, high-
dimensional optimization problems.
3.3. Process and characteristics of the hybrid
algorithm
In high-dimensional complex optimization problems, a
single optimization strategy often presents a trade-off
between search ability and convergence efficiency. Local
gradient optimization methods (such as Nadam) offer
rapid convergence but are prone to becoming trapped in
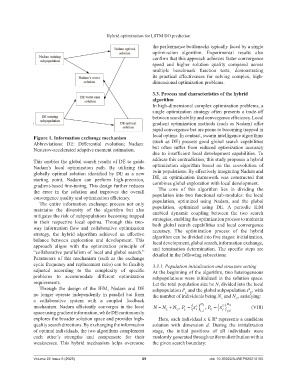
Figure 1. Information exchange mechanism local optima. In contrast, swarm intelligence algorithms
Abbreviations: DE: Differential evolution; Nadam: (such as DE) possess good global search capabilities
Nesterov-accelerated adaptive moment estimation. but often suffer from reduced optimization accuracy
due to insufficient local development capabilities. To
This enables the global search results of DE to guide address this contradiction, this study proposes a hybrid
Nadam’s local optimization path. By utilizing the optimization algorithm based on the coevolution of
globally optimal solution identified by DE as a new twin populations. By effectively integrating Nadam and
starting point, Nadam can perform high-precision, DE, an optimization framework was constructed that
gradient-based fine-tuning. This design further reduces combines global exploration with local development.
the error in the solution and improves the overall The core of this algorithm lies in dividing the
convergence quality and optimization efficiency. population into two functional sub-modules: the local
The entire information exchange process not only population, optimized using Nadam, and the global
maintains the diversity of the algorithm but also population, optimized using DE. A periodic IEM
enabled dynamic coupling between the two search
mitigates the risk of subpopulations becoming trapped
in their respective local optima. Through this two- strategies, enabling the optimization process to maintain
way information flow and collaborative optimization both global search capabilities and local convergence
accuracy. The optimization process of the hybrid
strategy, the hybrid algorithm achieved an effective algorithm can be divided into five stages: initialization,
balance between exploration and development. This local development, global search, information exchange,
approach aligns with the optimization principle of and termination determination. The specific steps are
“collaborative parallelism of local and global search.” detailed in the following subsections.
Parameters of this mechanism (such as the exchange
cycle frequency and replacement ratio) can be flexibly 3.3.1. Population initialization and structure setting
adjusted according to the complexity of specific At the beginning of the algorithm, two heterogeneous
problems to accommodate different optimization subpopulations were initialized in the solution space.
requirements. Let the total population size be N, divided into the local
Through the design of the IEM, Nadam and DE subpopulation P and the global subpopulation P , with
L
G
no longer operate independently in parallel but form the number of individuals being N and N , satisfying:
a collaborative system with a coupled feedback L G
mechanism. Nadam efficiently converges in the local N N N , P , P N G (VIII)
L
x
x
N L
G
G
i
L
j
L
G
space using gradient information, while DE continuously i1 j1
explores the broader solution space and provides high- Here, each individual x ∈ R represents a candidate
d
quality search directions. By exchanging the information solution with dimension d. During the initialization
of optimal individuals, the two algorithms complement stage, the initial positions of all individuals were
each other’s strengths and compensate for their randomly generated through uniform distribution within
weaknesses. This hybrid mechanism helps overcome the given search boundary:
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 69 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025210165