Page 11 - AJWEP-v22i2
P. 11
Traditional wisdom on managing soil and water
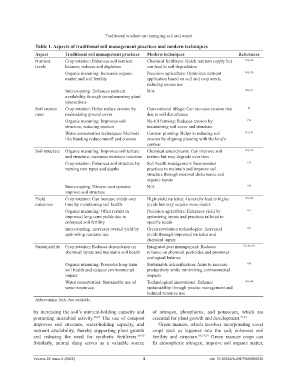
Table 1. Aspects of traditional soil management practices and modern techniques
Aspect Traditional soil management practices Modern techniques References
Nutrient Crop rotation: Enhances soil nutrient Chemical fertilizers: Quick nutrient supply but 118,148
levels balance; reduces soil depletion can lead to soil degradation
Organic manuring: Increases organic Precision agriculture: Optimizes nutrient 149,150
matter and soil fertility application based on soil and crop needs,
reducing excess use
Intercropping: Enhances nutrient N/A 150,151
availability through complementary plant
interactions
Soil erosion Crop rotation: Helps reduce erosion by Conventional tillage: Can increase erosion risk 32
rates maintaining ground cover due to soil disturbance
Organic manuring: Improves soil No-till farming: Reduces erosion by 152
structure, reducing erosion maintaining soil cover and structure
Water conservation techniques: Methods Contour plowing: Helps in reducing soil 153,154
like bunding reduce runoff and erosion erosion by aligning plowing with the land’s
contour
Soil structure Organic manuring: Improves soil texture Chemical amendments: Can improve soil 155,156
and structure; increases moisture retention texture but may degrade over time
Crop rotation: Enhances soil structure by Soil health management: Incorporates 157
varying root types and depths practices to maintain and improve soil
structure through minimal disturbance and
organic inputs
Intercropping: Diverse root systems N/A 158
improve soil structure
Yield Crop rotation: Can increase yields over High-yield varieties: Generally lead to higher 159,160
outcomes time by maintaining soil health yields but may require more inputs
Organic manuring: Often results in Precision agriculture: Enhances yield by 161
improved long-term yields due to optimizing inputs and practices tailored to
enhanced soil fertility specific needs
Intercropping: Increases overall yield by Green revolution technologies: Increased 162
optimizing resource use yields through improved varieties and
chemical inputs
Sustainability Crop rotation: Reduces dependency on Integrated pest management: Reduces 25,142,163
chemical inputs and maintains soil health reliance on chemical pesticides and promotes
ecological balance
Organic manuring: Promotes long-term Sustainable intensification: Aims to increase 164
soil health and reduces environmental productivity while minimizing environmental
impact impacts
Water conservation: Sustainable use of Technological innovations: Enhance 165,166
water resources sustainability through precise management and
reduced resource use
Abbreviation: N/A: Not available.
by increasing the soil’s nutrient-holding capacity and of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are
promoting microbial activity. 66,67 The use of compost essential for plant growth and development. 71,72
improves soil structure, water-holding capacity, and Green manure, which involves incorporating cover
nutrient availability, thereby supporting plant growth crops such as legumes into the soil, enhances soil
and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. 68-70 fertility and structure. 49,73,74 Green manure crops can
Similarly, animal dung serves as a valuable source fix atmospheric nitrogen, improve soil organic matter,
Volume 22 Issue 2 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025060035