Page 218 - AJWEP-v22i2
P. 218
Melnik, et al.
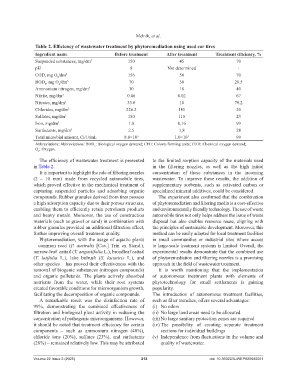
Table 2. Efficiency of wastewater treatment by phytoremediation using used car tires
Ingredient name Before treatment After treatment Treatment efficiency, %
Suspended substances, mg/dm 3 150 45 70
рН 8 Not determined -
COD, mg О /dm 3 156 50 70
2
BOD , mg О /dm 3 70 50 28.5
2
5
Ammonium nitrogen, mg/dm 3 30 18 40
Nitrite, mg/dm 3 0.06 0.02 67
Nitrates, mg/dm 3 33.6 10 70.2
Chlorides, mg/dm 3 226.2 181 20
Sulfates, mg/dm 3 150 115 23
Iron, mg/dm 3 1.8 0,16 99
Surfactants, mg/dm 3 2.5 1,8 28
Total microbial amount, CFU/mL 8.8×10 5 1.0×10 3 99
Abbreviations: Abbreviations: BOD : Biological oxygen demand; CFU: Colony-forming units; COD: Chemical oxygen demand;
5
O : Oxygen.
2
The efficiency of wastewater treatment is presented to the limited sorption capacity of the materials used
in Table 2. in the filtering nozzles, as well as the high initial
It is important to highlight the role of filtering nozzles concentration of these substances in the incoming
(2 – 10 mm) made from recycled automobile tires, wastewater. To improve these results, the addition of
which proved effective in the mechanical treatment of supplementary sorbents, such as activated carbon or
capturing suspended particles and adsorbing organic specialized mineral additives, could be considered.
compounds. Rubber granules derived from tires possess The experiment also confirmed that the combination
a high adsorption capacity due to their porous structure, of phytoremediation and filtering media is a cost-effective
enabling them to efficiently retain petroleum products and environmentally friendly technology. The use of waste
and heavy metals. Moreover, the use of construction automobile tires not only helps address the issue of waste
materials (such as gravel or sand) in combination with disposal but also enables resource reuse, aligning with
rubber granules provided an additional filtration effect, the principles of sustainable development. Moreover, this
further improving overall treatment quality. method can be easily adapted for local treatment facilities
Phytoremediation, with the usage of aquatic plants in small communities or industrial sites where access
– common reed (P. australis [Cav.] Trin ex Stend.), to large-scale treatment systems is limited. Overall, the
narrow-leaf cattail (T. angustifolia L.), broadleaf cattail experimental results demonstrate that the combined use
(T. latifolia L.), lake bulrush (S. lacustris L.), and of phytoremediation and filtering nozzles is a promising
other species – has proved their effectiveness with the approach in the field of wastewater treatment.
removal of biogenic substances (nitrogen compounds) It is worth mentioning that the implementation
and organic pollutants. The plants actively absorbed of autonomous treatment plants with elements of
nutrients from the water, while their root systems phytotechnology for small settlements is gaining
created favorable conditions for microorganism growth, popularity.
facilitating the decomposition of organic compounds. The introduction of autonomous treatment facilities,
A remarkable result was the disinfection rate of such as filter trenches, offers several advantages:
99%, demonstrating the combined effectiveness of (i) No odors
filtration and biological plant activity in reducing the (ii) No large land areas need to be allocated
concentration of pathogenic microorganisms. However, (iii) No large sanitary protection zones are required
it should be noted that treatment efficiency for certain (iv) The possibility of creating separate treatment
components – such as ammonium nitrogen (40%), sections for individual buildings
chloride ions (20%), sulfates (23%), and surfactants (v) Independence from fluctuations in the volume and
(28%) – remained relatively low. This may be attributed quality of wastewater.
Volume 22 Issue 2 (2025) 212 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025080051