Page 215 - AJWEP-v22i2
P. 215
Recycled tires for wastewater treatment
In Ukraine, Constructed Wetlands treatment systems types of bioplateaus. Systems incorporating HAP are
are referred to as bioengineered treatment plants (BTP). effectively employed for the additional purification of
The operating principle of these systems is based on wastewater following traditional treatment methods.
harnessing natural self-purification processes that occur Bioplateau systems not only water-air HAP (such as
within the filter layer, which serves as a substrate for reeds, cattails, bulrushes, and sedges) but also various
the development of biogeocenoses of HAP. Table 1 types of submerged vegetation, including redwood,
provides an overview of the main purification systems watercress, hornwort, and others.
that utilize phytoremediation. 23 The design characteristics and technological
At present, several types of BTP have been differences in the construction and operation of
developed, each with various treatment conditions and treatment facilities using HAP, similar to Constructed
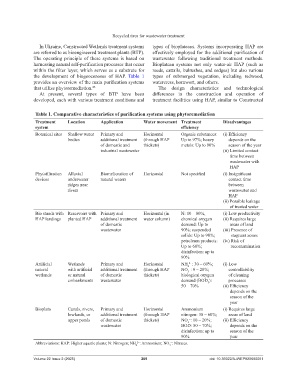
Table 1. Comparative characteristics of purification systems using phytoremediation
Treatment Location Application Water movement Treatment Disadvantages
system efficiency
Botanical sites Shallow water Primary and Horizontal Organic substances: (i) Efficiency
bodies additional treatment (through HAP Up to 97%; heavy depends on the
of domestic and thickets) metals: Up to 90% season of the year
industrial wastewater (ii) Limited contact
time between
wastewater with
HAP
Phytofiltration Alluvial Biomelioration of Horizontal Not specified (i) Insignificant
devices underwater natural waters contact time
ridges near between
rivers wastewater and
HAP
(ii) Possible leakage
of treated water
Bio stands with Reservoirs with Primary and Horizontal (in N: 10 – 80%, (i) Low productivity
HAP landings planted HAP additional treatment water column) chemical oxygen (ii) Requires large
of domestic demand: Up to areas of land
wastewater 90%; suspended (iii) Presence of
solids: Up to 98%; stagnant zones
petroleum products: (iv) Risk of
Up to 60%; recontamination
disinfection: up to
90%
Artificial Wetlands Primary and Horizontal NH : 30 – 60%; (i) Low
2−
4
natural with artificial additional treatment (through HAP NO : 0 – 20%; controllability
−
3
wetlands or natural of domestic thickets) biological oxygen of cleaning
embankments wastewater demand (BOD ): processes
5
50 – 70% (ii) Efficiency
depends on the
season of the
year
Bioplato Canals, rivers, Primary and Horizontal Ammonium (i) Requires large
lowlands, or additional treatment (through HAP nitrogen: 30 – 60%; areas of land
upper ponds of domestic thickets) NO : 10 – 20%; (ii) Efficiency
−
3
wastewater BOD: 50 – 70%; depends on the
disinfection: up to season of the
90% year
Abbreviations: HAP: Higher aquatic plants; N: Nitrogen; NH : Ammonium; NO : Nitrates.
2−
−
3
4
Volume 22 Issue 2 (2025) 209 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025080051