Page 11 - AN-1-2
P. 11
Advanced Neurology Pantothenic acid in kainic acid-induced epilepsy
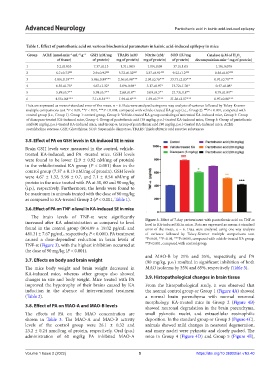
Table 1. Effect of pantothenic acid on various biochemical parameters in kainic acid‑induced epilepsy in mice
Group AChE (nmol·min ·mL ·g GSH (nM/mg TBARS (nM/ Nitrite (nM/ SOD (IU/mg Catalase (μM of H O 2
−1
−1
−1
2
of tissue) of protein) mg of protein) mg of protein) of protein) decomposition·min ·mg of protein)
−1
1 3.2±0.853 7.37±0.13 1.31±0.05 1.19±0.08 37.3±1.05 1.18±0.076
2 6.7±0.73 ### 2.9±0.92 ### 3.72±0.32 ### 3.37±0.91 ### 9.52±1.2 ### 0.36±0.07 ###
3 4.89±0.19*** 5.86±0.89*** 2.56±0.98*** 2.04±0.76*** 33.73±2.03*** 0.91±0.71***
4 6.55±0.75* 4.67±1.32* 3.09±0.98* 3.17±0.97* 13.72±1.76* 0.47±0.08*
5 5.89±0.7** 5.98±0.7** 2.68±0.4** 3.09±0.3** 21.73±1.8** 0.79±0.04**
6 4.53±0.8*** 7.1±0.54*** 1.94±0.8*** 1.93±0.7*** 31.36±2.17*** 0.97±0.06***
Data are expressed as means±standard error of the mean, n = 6. Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey-Kramer
multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with vehicle-treated KA group (i.e., Group 2). P < 0.001, compared with
###
control group (i.e., Group 1). Group 1: control group, Group 2: Vehicle-treated KA group consisting of untreated KA-induced mice, Group 3: Group
of diazepam-treated KA-induced mice, Group 4: Group of pantothenic acid (30 mg/kg, p.o.)-treated KA-induced mice, Group 5: Group of pantothenic
acid (60 mg/kg, p.o.)-treated KA-induced mice, and Group 6: Group of pantothenic acid (90 mg/kg, p.o.)-treated KA-induced mice. AChE
acetylcholine esterase, GSH: Glutathione, SOD: Superoxide dismutase, TBARS: Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
3.5. Effect of PA on GSH levels in KA-induced SE in mice
Brain GSH levels were measured in the control, vehicle-
treated KA-induced, and PA -treated mice. GSH levels
were found to be lower (2.9 ± 0.92 nM/mg of protein)
in the vehicle-treated KA group (P < 0.001) than in the
control group (7.37 ± 0.13 nM/mg of protein). GSH levels
were 4.67 ± 1.32, 5.98 ± 0.7, and 7.1 ± 0.54 nM/mg of
protein in the mice treated with PA at 30, 60 and 90 mg/kg
(i.p.), respectively. Furthermore, the levels were found to
be maximum in animals treated with the dose of 90 mg/kg
as compared to KA-treated Group 2 (P < 0.001, Table 1).
3.6. Effect of PA on TNF-α level in KA-induced SE in mice
The brain levels of TNF-α were significantly
increased after KA administration as compared to level Figure 3. Effect of 7-day pretreatment with pantothenic acid on TNF-α
level in KA-induced SE in mice. Data are expressed as means ± standard
found in the control group (804.09 ± 19.02 pg/mL and error of the mean, n = 6. Data were analyzed using one-way analysis
481.31 ± 7.67 pg/mL, respectively, P < 0.001). PA treatment of variance followed by Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test.
caused a dose-dependent reduction in brain levels of *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, compared with vehicle-treated KA group.
TNF-α (Figure 3), with the highest inhibition occurred at ### P<0.001, compared with control group.
the dose of 90 mg/kg (P < 0.001).
and MAO-B by 21% and 35%, respectively, and PA
3.7. Effects on body and brain weight (90 mg/kg, p.o.) resulted in significant inhibition of both
The mice body weight and brain weight decreased in MAO isoforms by 35% and 65%, respectively (Table 3).
KA-induced mice, whereas other groups also showed
changes in size and body weight. Mice treated with PA 3.9. Histopathological changes in brain tissue
improved the hypotrophy of their brains caused by KA From the histopathological study, it was observed that
induction in the absence of interventional treatment the normal control group or Group 1 (Figure 4A) showed
(Table 2). a normal brain parenchyma with normal neuronal
morphology. KA-treated mice in Group 2 (Figure 4B)
3.8. Effect of PA on MAO-A and MAO-B levels showed neuronal degradation in the brain parenchyma,
The effects of PA on the MAO concentration are small pyknotic nuclei, and extracellular eosinophilic
shown in Table 3. The MAO-A and MAO-B activity deposition. In the standard group or Group 3 (Figure 4C),
levels of the control group were 26.1 ± 0.32 and animals showed mild changes in neuronal degeneration,
23.2 ± 0.24 nmol/mg of protein, respectively. Oral (p.o.) and many nuclei were pyknotic and closely packed. The
administration of 60 mg/kg PA inhibited MAO-A mice in Group 4 (Figure 4D) and Group 5 (Figure 4E),
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i2.40