Page 59 - AN-1-3
P. 59
Advanced Neurology Targets and medications for AVM of CNS
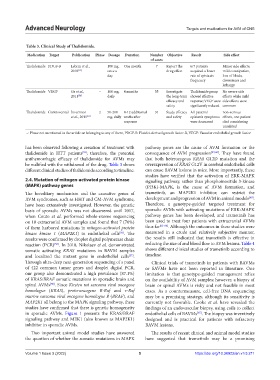
Table 3. Clinical Study of Thalidomide.
Medication Target Publication Phase Dosage Duration Number Objective Result Side effect
of cases
Thalidomide PDGF-B Lebrin et al., – 100 mg, One month 7 Report the 6/7 patients Minor side effects:
2010 [52] once a drug effect acquired a lower mild constipation,
day rate of epistaxis loss of libido,
frequency drowsiness and
lethargy
Thalidomide VEGF Ge et al., – 100 mg, 4 months 55 Investigate Thalidomide group No severe side
2011 [54] daily the long-term showed effective effects while mild
efficacy and response; VEGF were side effects were
safety significantly reduced common
Thalidomide Controversial Invernizzi 2 50-200 8-12 additional 31 Study efficacy All patients’ non-serious
et al., 2015 [53] mg, daily weeks after and safety epistaxis symptoms effects, one patient
response were decreased died considering
unrelated
–: Phase not mentioned in the article or belonging to any of them, PDGF-B: Platelet-derived growth factor-B, VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor
has been observed following a cessation of treatment with pathway genes are the cause of AVM formation or the
thalidomide in HTT patients ; therefore, the potential consequence of AVM progression [59,60] . They have found
[52]
antihemorrhagic efficacy of thalidomide for AVMs may that both heterozygous KRAS G12D mutation and the
be nullified with the withdrawal of the drug. Table 3 shows overexpression of KRAS G12V in cerebral endothelial cells
different clinical studies of thalidomide according to timeline. can cause BAVM lesions in mice. More importantly, these
studies have verified that the activation of ERK-MAPK
2.4. Mutation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, rather than phosphoinositide 3-kinase
(MAPK) pathway genes (PI3K)-MAPK, is the cause of AVM formation, and
The hereditary mechanism and the causative genes of trametinib, an MAP2K1 inhibitor, can restrict the
[60]
AVM syndromes, such as HHT and CM-AVM syndrome, development and progression of AVM in animal models .
have been extensively investigated. However, the genetic Therefore, a genotype-guided targeted treatment for
basis of sporadic AVMs was not discovered until 2017, sporadic AVMs with activating mutations of ERK-MAPK
when Couto et al. performed whole-exome sequencing pathway genes has been developed, and trametinib has
on 10 extracranial AVM samples and found that 7 (70%) been used to treat four patients with extracranial AVMs
of them harbored mutations in mitogen-activated protein thus far [61-64] . Although the outcomes in these studies were
kinase kinase 1 (MAP2K1) in endothelial cells . The measured in a crude and relatively subjective manner,
[56]
results were confirmed by droplet digital polymerase chain the results still indicated that trametinib is effective in
reaction (PCR) . In 2018, Nikolaev et al. demonstrated reducing the size of and blood flow to AVM lesions. Table 4
[56]
somatic activating KRAS mutations in BAVM samples shows different clinical studies of trametinib according to
and localized the mutant gene in endothelial cells . timeline.
[57]
Through ultra-deep next-generation sequencing of a panel Clinical trials of trametinib in patients with BAVMs
of 422 common tumor genes and droplet digital PCR, or SAVMs have not been reported in literature. One
our group also demonstrated a high prevalence (87.1%) limitation is that genotype-guided management relies
of KRAS/BRAF somatic mutations in sporadic brain and on the availability of AVM samples; however, a biopsy of
spinal AVMs . Since Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene brain or spinal AVMs is risky and not feasible in most
[58]
homologue (KRAS), proto-oncogene B-Raf and v-Raf cases. As a countermeasure, cell-free DNA sequencing
murine sarcoma viral oncogene homologue B (BRAF), and may be a promising strategy, although its sensitivity is
MAP2K1 all belong to the MAPK signaling pathway, these currently not favorable. Cooke et al. have revealed the
studies have confirmed that there is genetic homogeneity findings of an endovascular biopsy, using coils to collect
in sporadic AVMs. Figure 1 presents the KRAS/BRAF endothelial cells of BAVMs . The biopsy was inventively
[65]
signaling pathway and MEK1 (also known as MAP2K1) designed and is practical for patients with refractory
inhibitor in sporadic AVMs. BAVM lesions.
Two important animal model studies have answered The results of recent clinical and animal model studies
the question of whether the somatic mutations in MAPK have suggested that trametinib may be a promising
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2022) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i3.211