Page 10 - AN-2-1
P. 10
Advanced Ne
Advanced Neurologyurology The AIS structure and function
2. Structure of AIS that, the dynein regulator nuclear distribution element-like
1 (NDEL1) localizes to the AIS through interaction with
The molecular structure of the AIS is relatively complex and AnkG and controls cargo transport at the AIS .
[16]
is maintained by the accumulation of ankyrin G (AnkG)
and βIV-spectrin [6,7] . AnkG, a product of the ANK3 gene, is In addition, there is a layer of specialized extracellular
an anchoring protein at the AIS . It forms a “scaffolding” matrix anchored to the AIS that promotes and regulates
[8]
structure with βIV-spectrin to anchor ion channels the production of APs by various ion channels, such as
to the actin cytoskeleton. AnkG has three isoforms in Na , K, and calcium channels (Ca ) [17-20] , allowing neurons
v
v
v
[21]
mammals: 190-kDa AnkG, which is distributed in the to generate a wide variety of AP waveforms . Although
cytoplasm; and 270-kDa and 480-kDa AnkG, which are the basic components of the AIS have been known for
the major isoforms that are specifically located at the AIS more than two decades, recent studies have indicated
and nodes of Ranvier [8-10] . Following axon differentiation, an increasing complexity of its types and the molecular
AnkG begins to cluster at the proximal end of the axon composition and distribution of ion channels enriched
and then recruits the other components of AIS [11,12] . The within it.
aminoterminal end of AnkG inserts into the actin/spectrin 3. Ion channels in the AIS
submembrane scaffold and anchors specific membrane
proteins, including γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA ) The entire AIS is enriched with many sodium channels of
A
[22]
receptors, voltage-gated sodium (Na ), and potassium (K ) different subtypes . AnkG binds to the interaction motif
v
v
channels, as well as cellular adhesion molecules (CAMs), within the II-III intracellular loop of Na channels [23-26] .
v
specifically the 186 kDa isoform of neurofascin 186 Experiments have shown that the concentration of sodium
+
(NF-186) and neuronal (Nr)CAM, to the AIS (Figure 1). ion (Na ) channels in neuronal AIS is approximately 19-fold
[13]
[27]
Moreover, Wang et al. reported that neurons with αII of that in the cell body , 50-fold of that in the proximal
[29]
[28]
spectrin deletion also showed the absence of AnkG, dendrite , and 30-fold of that in the distal axon . The
+
suggesting that αII spectrin and βIV-spectrin can interact main subtypes of Na channels at the AIS are Na 1.1,
v
[30,31]
to form spectrin tetramers that link adjacent actin rings Na 1.2, and Na 1.6 . During different developmental
v
v
and are required for AnkG clustering in the AIS . stages, the expression and subcellular distribution of
[14]
+
various subtypes of Na channels vary. For example, during
In addition to actin, AnkG also interacts with early neuronal development, Na 1.2 channels are initially
v
microtubules through microtubule-associated proteins. For found in the AIS, while Na 1.6 is the dominant subtype in
v
instance, a previous study has shown that the microtubule mature neurons [20,29,30,32,33] . Moreover, in cortical neurons,
plus-end-binding (EB) proteins EB1 and EB3 are highly high-threshold Na 1.2 channels are preferentially located
v
concentrated in mature AIS and can directly bind to at the proximal end of the AIS, while low-threshold Na 1.6
v
AnkG, thus suggesting that EB1 and EB3 can stabilize the channels are found at the distal end of the AIS . Na
[27]
v
structure and microtubule network together . Not only channels are primarily responsible for the initiation of
[15]
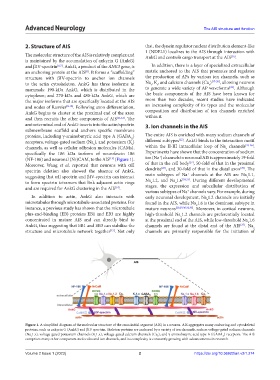
Figure 1. A simplified diagram of the molecular structure of the axon initial segment (AIS) in a neuron. AIS aggregates many anchoring and cytoskeletal
proteins, such as ankyrin G (AnkG) and βIV spectrin. Skeleton proteins are anchored by a variety of ion channels, such as voltage-gated sodium channels
(Na 1.x), voltage-gated potassium channels (K 1.x), voltage-gated calcium channels (Ca ), and γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA ) receptors. The AIS
v
v
A
v
comprises many other component molecules and ion channels, and its complexity is constantly growing with advancements in research.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v2i1.274