Page 83 - AN-2-1
P. 83
Advanced Neurology Choreoathetosis with contralateral substantia nigra infarction
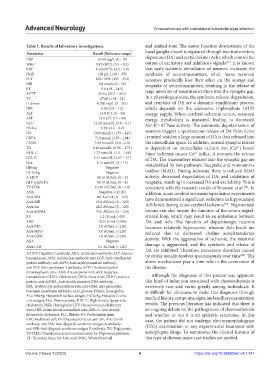
Table 1. Results of laboratory investigations. and unified state. The motor function downstream of the
Parameter Result (Reference range) basal ganglia circuit is regulated through two transmitters,
CRP <0.50 mg/L (0 – 10) dopamine (DA) and acetylcholine (Ach), which control the
[17]
WBC 9.17×10 /L (3.5 – 9.5) output of excitatory and inhibitory signals . It is known
9
12
RBC 4.62×10 /L (4.3 – 5.8) that early ischemic stimulation of neurons increases the
HGB 138 g/L (130 – 175) synthesis of neurotransmitters, while nerve terminal
PLT 236×10 /L (125 – 350) synapses practically lose their effect on the storage and
9
ESR 3.8 mm/h (0 – 15) reuptake of neurotransmitters, resulting in the release of
PT 9.6 s (9 – 14.5) large amounts of neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap.
APTT 28.8 s (22.5 – 40.5)
TT 17.00 s (14 – 21) In a physiological state, the synthesis, release, degradation,
D-dimer 0.320 mg/L (0 – 0.5) and reuptake of DA are a dynamic equilibrium process,
INR 0.82 (0.8 – 1.5) which depends on the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
ALT 13.0 U/L (9 – 50) energy supply. When cerebral ischemia occurs, neuronal
AST 13.0 U/L (15 – 40) energy metabolism is impaired, leading to decreased
GLU 12.28 mmol/L (3.8 – 6.1) Na -K -ATPase activity. The automatic depolarization of
+
+
HbA1c 9.3% (4.2 – 6.2)
UA 134.0 µmol/L (135 – 425) neurons triggers a spontaneous release of DA from nerve
CREA 71.0 µmol/L (59 – 104) terminal vesicles; a large amount of DA is thus released into
CHOL 5.59 mmol/L (2.8 – 6.0) the intercellular space. In addition, normal synaptic release
2+
TG 0.46 mmol/L (0.56 – 1.71) is dependent on intracellular calcium ion (Ca ) levels.
HDL-C 1.73 mmol/L (1.2 – 1.68) Since ischemia causes Ca influx, it prompts the release
2+
LDL-C 3.41 mmol/L (2.07 – 3.1) of DA. The transmitters released into the synaptic gap are
Hcy 6.15 µmol/L (5 – 14) metabolized by two pathways: Reuptake and monoamine
HBsAg Negative
HCVcAg Negative oxidase (MAO). During ischemia, there is reduced MAO
A-HCV 0.010 AU/mL (0 – 5) activity, decreased degradation of DA, and inhibition of
HIV combi PT 0.010 AU/mL (0 – 1) reuptake, resulting in increased DA and excitability. This is
TP-CLIA 0.240 mIU/mL (0 – 10) consistent with the research results of Brannan et al. . In
[18]
ANA Negative (<1:100) addition, acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion experiments
Anti-SSA 4.0 AU/mL (0 – 120) have demonstrated a significant reduction in hippocampal
Anti-SSB 23.0 AU/mL (0 – 120) [19]
Anti-Sm 42.0 AU/mL (0 – 120) Ach levels during acute cerebral ischemia . Nigrostriatal
Anti-dsDNA 70.0 AU/mL (0 – 120) lesions can also impair the function of the striato-nigral-
RF 1.2 IU/mL (<20) striatal loop, which may result in an imbalance between
ASO 18.0 IU/mL (<200) DA and Ach. The function of dopaminergic neurons
Anti-PR3 3.0 AU/mL (<120) becomes relatively hyperactive, whereas Ach levels are
Anti-MPO 3.0 AU/mL (<120) reduced due to decreased choline acetyltransferase
Anti-GBM 1.0 AU/mL (<120)
AKA Negative activity. With the aggravation of ischemia, the neuronal
Anti-CCP 1.1 AU/mL (< 120) damage is aggravated, and the synthesis and release of
DA are inhibited. Therefore, movement disorders caused
A-HCV: Hepatitis C antibody; AKA: Antikeratin antibody; ALT: Alanine by stroke usually resolves spontaneously over time . The
[20]
transaminase; ANA: Antinuclear antibody; anti-CCP: Anti-citrullinated
protein antibody; anti-MPO: Anti-myeloperoxidase antibody; above mechanisms play a joint role in the occurrence of
anti-PR3: Anti-proteinase-3 antibody; APTT: Activated partial the disease.
thromboplastin time; ASO: Antistreptolysin O; AST: Aspartate
transaminase; CHOL: Cholesterol; CREA: Creatinine; CRP: C-reactive Although the diagnosis of this patient was apparent,
protein; anti-dsDNA: Anti-double stranded DNA antibody; this kind of infarction associated with choreoathetosis is
ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; anti-GBM, anti-glomerular extremely rare and varies greatly among individuals. It
basement membrane antibody; GLU, glucose; HbA1c, hemoglobin is difficult for clinicians to make this diagnosis through
A1c; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HCVcAg: Hepatitis C virus medical history, symptoms, signs, and ancillary examination
core antigen; Hcy: Homocysteine; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein
cholesterol; HGB: Hemoglobin; HIV: Human immunodeficiency results. The previous literature has indicated that there is
virus; INR: International normalized ratio; LDL-C: Low-density an ongoing debate on the pathogenesis of choreoathetosis
lipoprotein cholesterol; PLT: Platelet; PT: Prothrombin time; and whether or not it is an epileptic syndrome. In this
RBC: Red blood cell; RF: Rheumatoid factor; anti-Sm: Anti-Smith case, the patient did not undergo electroencephalogram
antibody; anti-SSA: Anti-Sjögren’s syndrome antigen A antibody; (EEG) examination or any experimental treatment with
anti-SSB: Anti-Sjögren’s syndrome antigen B antibody; TG: Triglyceride;
TP-CLIA: Chemiluminescence immunoassay for Treponema pallidum; antiepileptic drugs. To summarize the clinical features of
TT: Thrombin time; UA: Uric acid; WBC: White blood cell this type of disease, more case studies are needed.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v2i1.141