Page 99 - AN-2-3
P. 99
Advanced Neurology eGFR and serum neurofilament light chain
Table 3. Multivariate analysis of the association between eGFR and sNfL
Variables Model 1 Model 2 Model 3
β (95% CI [upper P‑value β (95% CI [upper P‑value β (95% CI [upper P‑value
limit, lower limit]) limit, lower limit]) limit, lower limit])
eGFR −0.22 (−0.34, −0.10) 0.01 −0.2 (−0.31, −0.10) 0.01 −0.2 (−0.30, −0.10) <0.01
eGFR
Q1 1.00 (ref) 1.00 (ref) 1.00 (ref)
Q2 −6.06 (−11.20, −0.91) 0.03 −4.81 (−9.31, −0.30) 0.04 −4.8 (−9.21, −0.39) 0.03
Q3 −7.22 (−12.82, −1.61) 0.02 −7.05 (−12.33, −1.77) 0.01 −7.28 (−12.63, −1.92) 0.01
Q4 −5.8 (−10.60, −1.01) 0.03 −5.63 (−9.98, −1.29) 0.01 −5.78 (−10.24, −1.31) 0.01
Notes: Q1 (1.86–82.82), Q2 (82.82–98.39), Q3 (98.39–111.39), Q4 (111.39–159.93). Model 1: Adjust age + sex + education + marital; Model 2: Adjust
model 1 + drink+smoke + CKD + HF + MI + MetS + DM; Model 3: Adjust model 2 + hyperlipidemia + hypertension + stroke. CI: Confidence interval;
eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; sNfL: Serum neurofilament light chain.
Table 4. Threshold effect analysis of eGFR on sNfL by the two‑piecewise linear regression
Variable β (95% CI [upper limit, lower limit]) P‑value
Fitting by standard linear model −0.20 (−0.20, −0.10) <0.01
Fitting by two-piecewise linear model
Inflection point 59.9
eGFR <59.9 −1.00 (−1.30, −0.80) <0.01
eGFR >59.9 −0.10 (−0.10,0.00) 0.01
Log-likelihood ratio <0.001
Abbreviations: CI: Confidence interval; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate.
mechanism is that hypertension could lead to vascular
damage and inflammation, contributing to neuronal injury
and increased sNfL levels in individuals with decreased
eGFR. Neuronal damage can result in an elevation of sNfL
levels [20,21] . Hypertension can increase the expression of
adhesion factors in brain endothelial cells, leading to platelet
deposition. This, in turn, activates glial cells and NF-κB signal
transduction, ultimately resulting in neuronal damage .
[22]
Furthermore, sustained intracranial hypertension can cause
cerebral perfusion damage and neuronal injury, resulting in
secondary brain injury . It has been found that hypertension
[23]
is associated with sNfL levels, and previous studies have
reported a correlation between sNfL levels in cerebrospinal
fluid and idiopathic intracranial hypertension [24,25] .
In previous studies, age has been identified as an
important factor affecting sNfL levels, with a more
significant impact observed in participants aged 60 or
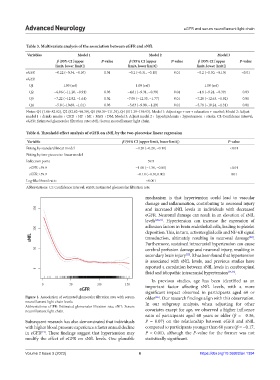
Figure 1. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate with serum older . Our research findings align with this observation.
[26]
neurofilament light chain levels. In our subgroup analysis, when adjusting for other
Abbreviations: eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; sNfL: Serum
neurofilament light chain. covariates except for age, we observed a higher influence
ratio of participants aged 60 years or older (β = −0.36,
Subsequent research has also demonstrated that individuals P = 0.07) on the relationship between eGFR and sNfL
with higher blood pressure experience a faster annual decline compared to participants younger than 60 years (β = −0.17,
in eGFR . These findings suggest that hypertension may P < 0.01), although the P-value for the former was not
[19]
modify the effect of eGFR on sNfL levels. One plausible statistically significant.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1394