Page 109 - AN-3-1
P. 109
Advanced Neurology MNS in patients with anxiety and depressive symptoms
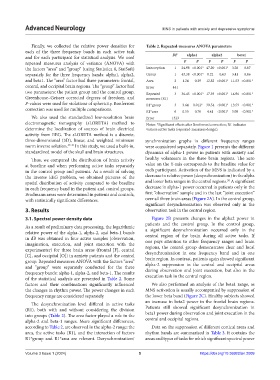
Finally, we collected the relative power densities for Table 2. Repeated‑measures ANOVA parameters
each of the three frequency bands in each active task
and for each participant for statistical analysis. We used DF alpha1 alpha2 beta1
repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with F P F P F P
the factors “area” and “group” (using Statistica 8, StatSoft) Interception 1 24.98 <0.001* 47.20 <0.001* 3.28 0.07
separately for the three frequency bands: alpha1, alpha2, Group 1 43.38 <0.001* 0.22 0.63 3.41 0.06
and beta1. The “area” factor had three parameters: frontal, Area 2 1.24 0.29 12.82 <0.001* 11.53 <0.001*
central, and occipital brain regions. The “group” factor had Error 441
two parameters: the patient group and the control group. Repeated 3 36.45 <0.001* 17.39 <0.001* 14.96 <0.001*
Greenhouse–Geisser corrected degrees of freedom, and measures (R1)
P-values were used for violations of sphericity. Bonferroni R1*group 3 3.64 0.012* 30.54 <0.001* 13.59 <0.001*
correction was used for multiple comparisons.
R1*area 6 0.55 0.76 4.41 <0.001* 5.08 <0.001*
We also used the standardized low-resolution brain Error 1323
electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA) method to Notes: *Significant effects after Bonferroni correction; R1 indicates
determine the localization of sources of brain electrical various active tasks (repeated-measures design).
activity from EEG. The sLORETA method is a discrete,
three-dimensional (3D), linear, and weighted minimum synchronization graphs in different frequency ranges
norm inverse solution. 47-49 In this study, we used a built-in, were considered separately. Figure 1 presents the different
standardized model of the skull and brain structures. dynamics of alpha-1 power in patients with anxiety and
Thus, we compared the distribution of brain activity healthy volunteers in the three brain regions. The zero
at baseline and when performing active tasks separately value on the Y-axis corresponds to the baseline value for
in the control group and patients. As a result of solving each participant. Activation of the MNS is indicated by a
the inverse EEG problem, we obtained pictures of the decrease in relative power (desynchronization) in the alpha
20
spatial distribution of activity compared to the baseline and lower beta ranges in the central regions. A significant
in each frequency band in the patient and control groups. decrease in alpha-1 power occurred in patients only in the
Brodmann areas were determined in patients and controls, first “observation” sample and in the last “joint execution”
with statistically significant differences. over all three brain areas (Figure 2A). In the control group,
significant desynchronization was observed only in the
3. Results observation task in the central region.
3.1. Spectral power density data Figure 2B presents changes in the alpha2 power in
patients and the control group. In the control group,
As a result of preliminary data processing, the logarithmic
relative power of the alpha-1, alpha-2, and beta-1 bands a significant desynchronization occurred only in the
central region of the brain during all active tasks. If
in dB was obtained in four active samples (observation, one pays attention to other frequency ranges and brain
imagination, execution, and joint execution with the
experimenter) for three brain areas (frontal [F], central regions, the control group demonstrates clear and local
[C], and occipital [O]) in anxiety patients and the control desynchronization in one frequency band and in one
brain region. In contrast, patients again showed significant
group. Repeated measures ANOVA with the factors “area” alpha-2 suppression in the central and occipital areas
and “group” were separately conducted for the three
frequency bands: alpha-1, alpha-2, and beta-1. The results during observation and joint execution, but also in the
of the statistical analysis are presented in Table 2. Some execution task in the central region.
factors and their combinations significantly influenced We also performed an analysis of the beta1 range, as
the changes in rhythm power. The power changes in each MNS activation is usually accompanied by suppression of
frequency range are considered separately. the lower beta band (Figure 2C). Healthy subjects showed
an increase in beta2 power in the frontal brain regions.
The desynchronization level differed in active tasks
(R1), both with and without considering the division Patients still showed significant desynchronization in
into groups (Table 2). The area factor played a role in the beta1 power during observation and joint execution in the
alpha-2 and beta-1 ranges. More significant differences, central and occipital regions.
according to Table 2, are observed in the alpha-2 range: the Data on the suppression of different cortical areas and
area, the active tasks (R1), and the interaction of factors rhythm bands are summarized in Table 3. It contains the
R1*group and R1*area are relevant. Desynchronization/ areas and types of tasks for which significant spectral power
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.2009