Page 115 - AN-3-2
P. 115
Advanced Neurology Cerebrovascular pathology biomarkers in post-COVID-19 patients
established that vaccination before SARS-CoV-2 infection Table 3. Distribution of the severity of COVID‑19 in
can reduce the risk of developing prolonged COVID-19. patients who had contracted a COVID‑19 infection based on
vaccination status
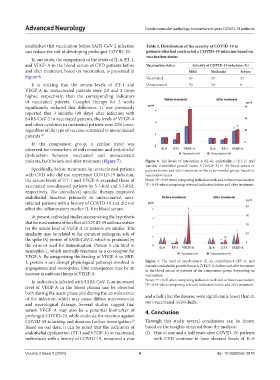
In our study, the comparison of the levels of IL-6, ET-1,
and VEGF-A in the blood serum of CVD patients before Vaccination status Severity of COVID‑19 infection (%)
and after treatment, based on vaccination, is presented in Mild Moderate Severe
Figure 6. Vaccinated 50 29 21
It is striking that the serum levels of ET-1 and Unvaccinated 70 30 0
VEGF-A in unvaccinated patients were 2.8 and 2 times
higher, respectively, than the corresponding indicators
of vaccinated patients. Complex therapy for 2 weeks
significantly reduced this difference. It was previously
reported that 3 months (90 days) after infection with
SARS-CoV-2 in vaccinated patients, the levels of VEGF-A
and other cytokines in vaccinated patients were 20% lower,
regardless of the type of vaccine, compared to unvaccinated
patients. 28
In the comparison group, a similar trend was
observed for biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial
dysfunction between vaccinated and unvaccinated
patients, both before and after treatment (Figure 7). Figure 6. The levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), endothelin-1 (ET-1), and
vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) in the blood serum of
Specifically, before treatment, in unvaccinated patients patients before and after treatment in the experimental group, based on
with CVD who did not experience COVID-19 infection, vaccination status
a
the serum levels of ET-1 and VEGF-A exceeded those of Notes: P < 0.05 when comparing indicators with and without vaccination;
vaccinated non-diseased patients by 3.7-fold and 5.2-fold, b P < 0.05 when comparing relevant indicators before and after treatment.
respectively. The introduced specific therapy improved
endothelial function primarily in unvaccinated, non-
infected patients with a history of COVID-19 and did not
affect the inflammatory marker IL-6 in blood serum.
At present, individual studies are examining the hypothesis
that the mechanisms of the effect of COVID-19 and vaccination
on the serum level of VEGF-A in patients are similar. This
similarity may be related to the common pathogenic role of
the spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2, which is produced by
the virus or used for immunization. Protein S can bind to
neuropilin-1, which normally functions as a co-receptor for
VEGF-A. By antagonizing the binding of VEGF-A to NRP-
1, protein S can disrupt physiological pathways involved in Figure 7. The level of interleukin-6 (IL-6), endothelin-1 (ET-1), and
angiogenesis and nociception. One consequence may be an vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) before and after treatment
in the blood serum of patients of the comparison group, depending on
increase in unbound forms of VEGF-A. vaccination
a
In individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2, an increased Notes: P < 0.05 when comparing indicators with and without vaccination;
b
level of VEGF-A in the blood plasma can be observed P < 0.05 when comparing relevant indicators before and after treatment.
both during the acute phase and during the convalescence
of the infection, which may cause diffuse microvascular and a half after the disease, were significantly lower than in
and neurological damage. Several studies suggest that non-vaccinated individuals.
serum VEGF A may also be a potential biomarker of 4. Conclusion
prolonged COVID-19, while evidence for vaccines against
COVID-19 is lacking and deserves further investigation. Through this study, several conclusions can be drawn
29
Based on our data, it can be noted that the indicators of based on the insights obtained from the analysis:
endothelial dysfunction (ET-1 and VEGF-A) in vaccinated (i) One to one and a half years after COVID-19, patients
individuals with a history of COVID-19, measured a year with CVD continue to have elevated levels of IL-6
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/an.2878