Page 82 - AN-3-2
P. 82
Advanced Neurology Neuropathy-reduced balance and gait
A B
C D
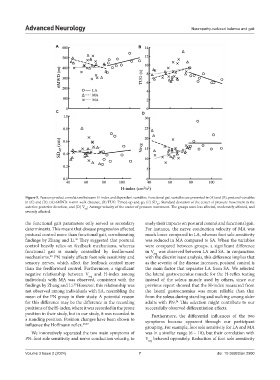
Figure 5. Pearson product correlations between H-index and dependent variables. Functional gait variables are presented in (A) and (B), postural variables
in (C) and (D). (A) 6MWD: 6-min walk distance, (B) TUG: Timed-up-and-go, (C) SD : Standard deviation of the center of pressure movement in the
AP
anterior-posterior direction, and (D) V : Average velocity of the center of pressure movement. The groups were less affected, moderately affected, and
avg
severely affected.
the functional gait parameters only served as secondary study their impacts on postural control and functional gait.
determinants. This meant that disease progression affected For instance, the nerve conduction velocity of MA was
postural control more than functional gait, corroborating much lower compared to LA, whereas foot sole sensitivity
findings by Zhang and Li. They suggested that postural was reduced in MA compared to SA. When the variables
20
control heavily relies on feedback mechanisms, whereas were compared between groups, a significant difference
functional gait is mainly controlled by feedforward in V was observed between LA and SA. In conjunction
avg
mechanisms. PN mainly affects foot sole sensitivity and with the discriminant analysis, this difference implies that
20
sensory nerves, which affect the feedback control more as the severity of the disease increases, postural control is
than the feedforward control. Furthermore, a significant the main factor that separates LA from SA. We selected
negative relationship between V and H-index among the lateral gastrocnemius muscle for the H-reflex testing
avg
individuals with MA was observed, consistent with the instead of the soleus muscle used by others, since our
findings by Zhang and Li. However, this relationship was previous report showed that the H-index measured from
20
not observed among individuals with SA, resembling the the lateral gastrocnemius was more reliable than that
mean of the PN group in their study. A potential reason from the soleus during standing and walking among older
for this difference may be the difference in the recording adults with PN. This selection might contribute to our
24
positions of the H-index, where it was recorded in the prone successfully observed differentiation effects.
position in their study, but in our study, it was recorded in Furthermore, the differential influences of the two
a standing position. Position changes have been shown to symptoms became apparent through our participant
influence the Hoffmann reflex. 26,27 grouping. For example, foot sole sensitivity for LA and MA
We innovatively separated the two main symptoms of was in a similar range (6 – 10), but their correlation with
PN: foot sole sensitivity and nerve conduction velocity, to V behaved oppositely. Reduction of foot sole sensitivity
avg
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/an.2900