Page 145 - AN-3-4
P. 145
Advanced Neurology Drosophila Sirtuin 1 and Alzheimer’s disease
A B
C
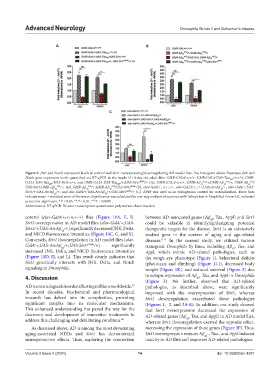
Figure 9. JNK and Notch expression levels in control and Sirt1 overexpressing/downregulating AD model flies. The histogram above illustrates JNK and
Notch gene expression levels quantified via RT-qPCR in the heads of 10-day-old adult flies: GMR-GAL4/+;+/+, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;+/+, GMR-
WT
GAL4-UAS-Tau /UAS-Sirt1;+/+, and GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Sirt1 RNAi /+ (A); GMR-GAL4/+;+/+, GMR-Aβ 42 k52 /+;GMR-Aβ 42 k53 /+, GMR-Aβ 42 k52 /
WT
WT
UAS-Sirt1;GMR-Aβ 42 k53 /+, and GMR-Aβ 42 k52 /+;GMR-Aβ 42 k53 /UAS-Sirt1 RNAi (B); elav-Gal4/+;+/+;+/+, elav-GAL4/+;+/+;UAS-ArcAβ /+, elav-Gal4/+;UAS-
42
Sirt1/+;UAS-ArcAβ /+, and elav-Gal4/+;UAS-ArcAβ /+;UAS-Sirt1 RNAi /+ (C). RP49 was used as an endogenous control for normalization. Error bars
42
42
indicate mean ± standard error of the mean. Significance was calculated by one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s test in GraphPad Prism 5.0, indicated
as ns: non-significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0001.
Abbreviation: RT-qPCR: Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
control (elav-Gal4/+;+/+;+/+) flies (Figure 10A, E, I). between AD-associated genes (Aβ , Tau, Appl) and Sirt1
42
Sirt1 overexpression in AD model flies (elav-Gal4/+;UAS- could be valuable in identifying/designing potential
Sirt1/+;UAS-ArcAβ /+) significantly decreased JNK, Delta, therapeutic targets for the disease. Sirt1 is an extensively
42
and NICD fluorescence intensities (Figure 10C, G, and K). studied gene in the context of aging and age-related
Conversely, Sirt1 downregulation in AD model flies (elav- diseases. 8-11 In the current study, we utilized various
Gal4/+;UAS-ArcAβ /+;UAS-Sirt1 RNAi /+) significantly transgenic Drosophila fly lines, including Aβ , Tau, and
42
42
increased JNK, Delta, and NICD fluorescence intensities Appl, which mimic AD-related pathologies, such as
(Figure 10D, H, and L). This result clearly indicates that the rough eye phenotype (Figure 1), behavioral deficits
Sirt1 genetically interacts with JNK, Delta, and Notch (phototaxis and climbing) (Figure 1I‑J), decreased body
signaling in Drosophila. weight (Figure 1K), and reduced survival (Figure 2) due
4. Discussion to ectopic expression of Aβ , Tau, and Appl in Drosophila
42
(Figure 3). We further, observed that AD-related
AD is a neurological disorder affecting millions worldwide. pathologies, as described above, were significantly
59
In recent decades, biochemical and pharmacological improved with the overexpression of Sirt1, whereas
research has delved into its complexities, providing Sirt1 downregulation exacerbated these pathologies
significant insights into its molecular mechanisms. (Figures 1, 2, and 3A‑E). In addition, our study showed
This enhanced understanding has paved the way for the that Sirt1 overexpression decreased the expression of
discovery and development of innovative treatments to AD-related genes (Aβ , Tau, and Appl) in AD model flies,
42
address this challenging and debilitating condition. 60 whereas Sirt1 downregulation exerted the opposite effect,
As discussed above, AD is among the most devastating increasing the expression of these genes (Figure 3F). Thus,
aging-associated NDDs and Sirt1 has demonstrated Sirt1 overexpression reduces Aβ -, Tau-, and Appl-induced
42
neuroprotective effects. Thus, exploring the connection toxicity in AD flies and improves AD-related pathologies.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 14 doi: 10.36922/an.4291