Page 141 - AN-3-4
P. 141
Advanced Neurology Drosophila Sirtuin 1 and Alzheimer’s disease
F
A B C D E
G H I
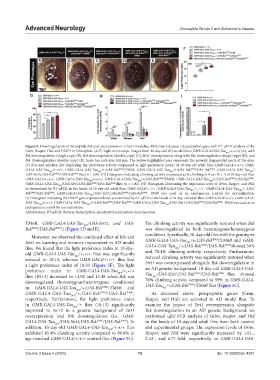
Figure 5. Downregulation of Drosophila Bsk and overexpression of Sirt1 modulate Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies, with RT-qPCR analysis of the
Grim, Reaper, Hid, and DIAP1 in Drosophila. (A-E) Light microscope images from 10-day-old AD model flies (GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;+/+)(A); with
WT
Bsk downregulation (single copy) (B); Bsk downregulation (double copy) (C); Sirt1 overexpression along with Bsk downregulation (single copy) (D); and
Bsk downregulation (double copy) (E). Scale bar indicates 100 μm. The yellow-highlighted area represents the severely degenerated parts of the eyes.
(F) Box-and-whisker plot displaying the phototaxis activity (expressed as light preference index) of 10-day-old adult flies: GMR-GAL4/+;+/+, GMR-
GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;+/+, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Bsk RNAi /TM6B, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi , GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /
WT
WT
WT
WT
UAS-Sirt1;UAS-Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi flies (n = 100). (G) Histogram indicating climbing activity (expressed as % climbing in 8 cm 10 s ) of 10-day-old flies:
−1
GMR-GAL4/+;+/+, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;+/+, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Bsk RNAi /TM6B, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi ,
WT
WT
WT
GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /UAS-Sirt1;UAS-Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi flies (n = 100). (H) Histogram illustrating the expression level of Grim, Reaper, and Hid,
WT
as determined by RT-qPCR in the heads of 10-day-old adult flies: GMR-GAL4/+;+/+, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;+/+, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-
WT
WT
Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi , GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /UAS-Sirt1;UAS-Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi . RP49 was used as an endogenous control for normalization.
WT
(I) Histogram indicating the DIAP1 gene expression level, as examined by RT-qPCR in the heads of 10-day-old adult flies: GMR-GAL4/+;+/+, GMR-GAL4-
UAS-Tau /+;+/+, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /UAS-Sirt1;UAS-Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi . RP49 was used as an
WT
WT
WT
endogenous control for normalization.
Abbreviation: RT-qPCR: Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
TM6B, GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /UAS-Sirt1, and UAS- The climbing activity was significantly restored when Bsk
WT
Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi ,) (Figure 5D and E). was downregulated in both heterozygous/homozygous
Moreover, we observed the combined effect of Bsk and conditions. Specifically, 10-day-old flies with the genotypes
RNAi
Sirt1 on learning and memory impairment in AD model GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Bsk /TM6B and GMR-
WT
RNAi
RNAi
flies. We found that the light preference index in 10-day- GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Bsk /UAS-Bsk showed 59%
WT
old GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;+/+ flies was significantly and 70.4% climbing activity, respectively. Furthermore,
WT
reduced to 10.13, whereas GMR-GAL4/+;+/+ flies had reduced climbing activity was significantly restored when
a light preference index of 18.50 (Figure 5F). The light Sirt1 was overexpressed alongside Bsk downregulation in
preference index in GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;+/+ an AD genetic background: 10-day-old GMR-GAL4-UAS-
WT
RNAi
RNAi
flies (10.13) increased to 13.92 and 15.48 when Bsk was Tau /UAS-Sirt1;UAS-Bsk /UAS-Bsk flies showed
WT
downregulated (homozygous/heterozygous conditions) 76% climbing activity compared to 59% in GMR-GAL4-
RNAi
in GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Bsk RNAi /TM6B and UAS-Tau /+;UAS-Bsk /TM6B flies (Figure 5G).
WT
WT
GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau WT /+;UAS-Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi , As discussed above, proapoptotic genes (Grim,
respectively. Furthermore, the light preference index Reaper, and Hid) are activated in AD model flies. To
in GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+ flies (10.13) significantly examine the impact of Sirt1 overexpression alongside
WT
improved to 16.72 in a genetic background of Sirt1 Bsk downregulation in an AD genetic background, we
overexpression and Bsk downregulation (i.e., GMR- performed qRT-PCR analysis of Grim, Reaper, and Hid
GAL4-UAS-Tau /UAS-Sirt1;UAS-Bsk RNAi /UAS-Bsk RNAi ). In in the heads of 10-day-old adult flies from both control
WT
addition, 10-day-old GMR-GAL4-UAS-Tau /+;+/+ flies and experimental groups. The expression levels of Grim,
WT
exhibited 45.4% climbing activity compared to 80.8% in Reaper, and Hid were significantly increased by 1.61-,
age-matched GMR-GAL4/+;+/+ control flies (Figure 5G). 2.43-, and 6.71-fold, respectively, in GMR-GAL4-UAS-
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 10 doi: 10.36922/an.4291