Page 90 - AN-3-4
P. 90
Advanced Neurology SARS-CoV-2 in age-associated neurodegeneration
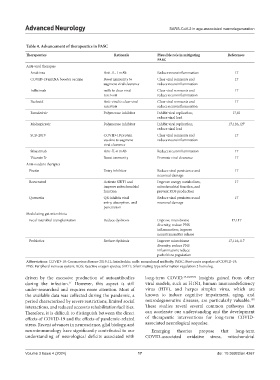
Table 4. Advancement of therapeutics in PASC
Therapeutics Rationale Plausible role in mitigating References
PASC
Anti-viral therapies
Anakinra Anti-IL-1 mAb Reduce neuroinflammation 17
COVID-19 mRNA booster vaccine Boost immunity to Clear viral remnants and 17
augment viral clearance reduce neuroinflammation
Infliximab mAb to clear viral Clear viral remnants and 17
reservoir reduce neuroinflammation
Paclovid Anti-viral to clear viral Clear viral remnants and 17
reservoir reduce neuroinflammation
Remdesivir Polymerase inhibitor Inhibit viral replication; 17,81
reduce viral load
Molnupiravir Polymerase inhibitor Inhibit viral replication; 17,126,127
reduce viral load
SCB-2019 COVID-19 protein Clear viral remnants and 17
vaccine to augment reduce neuroinflammation
viral clearance
Siltuximab Anti-IL-6 mAb Reduce neuroinflammation 17
Vitamin D Boost immunity Promote viral clearance 17
Anti-oxidant therapies
Fisetin Entry inhibitor Reduce viral persistence and 17
neuronal damage
Resveratrol Activate SIRT1 and Improve energy metabolism, 17
improve mitochondrial mitochondrial function, and
function prevent ROS production
Quercetin QR inhibits viral Reduce viral persistence and 17
entry, absorption, and neuronal damage
penetration
Modulating gut microbiota
Fecal microbial transplantation Reduce dysbiosis Improve microbiome 17,117
diversity; reduce PNS
inflammation; improve
neurotransmitter release
Probiotics Reduce dysbiosis Improve microbiome 17,116,117
diversity; reduce PNS
inflammation; reduce
pathobiont population
Abbreviations: COVID-19: Coronavirus disease-2019; IL: Interleukin; mAb: monoclonal antibody; PASC: Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19;
PNS: Peripheral nervous system; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SIRT1: Silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog.
driven by the excessive production of autoantibodies long-term COVID. 17,18,87,91 Insights gained from other
during the infection. However, this aspect is still viral models, such as H1N1, human immunodeficiency
11
under-researched and requires more attention. Most of virus (HIV), and herpes simplex virus, which are
the available data was collected during the pandemic, a known to induce cognitive impairment, aging, and
138
period characterized by severe restrictions, limited social neurodegenerative diseases, are particularly valuable.
interactions, and reduced access to rehabilitation facilities. These studies reveal several common pathways that
Therefore, it is difficult to distinguish between the direct can accelerate our understanding and the development
effects of COVID-19 and the effects of pandemic-related of therapeutic interventions for long-term COVID-
stress. Recent advances in neuroscience, glial biology, and associated neurological sequelae.
neuroimmunology have significantly contributed to our Emerging theories propose that long-term
understanding of neurological deficits associated with COVID-associated oxidative stress, mitochondrial
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 17 doi: 10.36922/an.4267