Page 79 - AN-4-1
P. 79
Advanced Neurology The South London Stroke Register
We describe the challenges of running a population- over time, in line with changing clinical pathways and
based stroke register, its key findings and its impact on diagnostic procedures. In earlier years, notifications
the delivery of effective stroke care locally, nationally and included community- and primary care-based sources,
internationally. such as general practitioners, community therapists and
coroners. Now, in the UK, all patients with stroke or TIA
2. Recruitment and follow-up – and its symptoms are expected to undergo brain imaging and be
changes and challenges over time referred to specialist hospital services. Case ascertainment
London as a location for a population-based register has therefore shifted further towards hospital-based
brings distinct advantages. The SLSR study area comprises sources. Apart from hospitals within the study area, those
a geographic area of South London (defined by electoral neighbouring the study area have been established as
wards) with a multi-ethnic population and areas of secondary recruitment sites to ensure outlying patients are
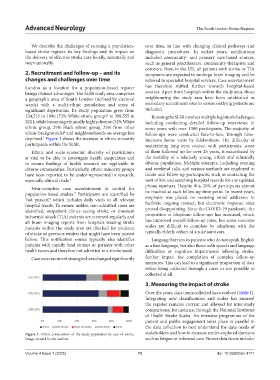
significant deprivation. Its study population grew from included.
234,533 in 1996 (72% White ethnic group) to 398,555 in Running the SLSR involves multiple logistical challenges,
3
2021, while becoming ethnically highly diverse (52% White including conducting detailed follow-up interviews, in
ethnic group, 25% Black ethnic group, 23% from other some years with over 1300 participants. The majority of
ethnic backgrounds) and neighbourhoods on average less follow-ups were conducted face-to-face, through time-
4
deprived. Figure 1 shows the increase in ethnic minority intensive home visits by fieldworkers. The difficulty of
5
participants within the SLSR. maintaining long-term contact with participants, some
Ethnic and socio-economic diversity of participants of them followed up for over 25 years, is exacerbated by
is vital to be able to investigate health inequalities and the mobility of a relatively young, urban and ethnically
to ensure findings of health research are applicable in diverse population. Multiple attempts, including evening
diverse communities. Particularly, ethnic minority groups and weekend calls, and various methods are employed to
have been reported to be under-represented in research, locate and follow-up participants, such as contacting the
especially clinical trials. 6 next of kin and searching hospital records for any updated
phone numbers. Despite this, 20% of participants cannot
Near-complete case ascertainment is central for
population-based studies. Participants are identified by be reached at each follow-up time point. In recent years,
7
‘hot pursuit’, which includes daily visits to all relevant emphasis was placed on securing email addresses to
8
hospital wards. To ensure milder, non-admitted cases are facilitate ongoing contact, but electronic response rates
identified, outpatient clinics seeing stroke or transient proved disappointing. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the
ischaemic attack (TIA) patients are screened regularly and proportion of telephone follow-ups has increased, which
all brain imaging reports from hospitals treating stroke has improved overall follow-up rates, but some outcome
patients within the study area are checked for evidence scales are difficult to complete by telephone with the
of stroke or previous strokes that might have been missed typically elderly cohort of stroke survivors.
before. This notification source typically also identifies Language barriers in patients who do not speak English
patients with rapidly fatal strokes or patients with other as a first language, but also those with speech and language
health issues and therefore not admitted to a stroke ward. difficulties or cognitive impairments following stroke,
Case ascertainment strategies have changed significantly further impact the completion of complex follow-up
measures. This can lead to a significant proportion of data
either being collected through a carer or not possible to
collected at all.
3. Measuring the impact of stroke
Over the years, data items collected have evolved (Table 1).
Integrating new classifications and scales has ensured
the register remains current and allowed for inter-study
comparisons, for instance, through the National Institutes
of Health Stroke Scales. An intensive programme of the
patient and public engagement takes place in parallel to
the data collection to best understand the data needs of
Figure 1. Ethnic composition of the study population by year of stroke. stakeholders and how to measure under-explored domains
Image created by the authors. such as fatigue or informal care. Newer data items include:
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 73 doi: 10.36922/an.4771