Page 62 - AN-4-2
P. 62
Advanced Neurology Brain bioavailability of targeted protein degraders
wrapped in myelin (a protective coating), and gray matter transcytosis-mediated transport. While venules tend to
23
forming the core, composed of neuron somas (the round, express genes involved in inflammation-related processes
central cell bodies). The different composition of neurons more abundantly, capillaries preferentially express genes
in each part causes the brain to appear as separate shades related to solute transport. Pericytes are located on the
24
of gray and white. abluminal surface of PCVs. Although they do not directly
contribute to barrier function, pericytes, in conjunction
3. Cerebral vasculature with astrocytes, produce substances that aid in recovery
13
Capillary segments in the human brain range in size from and repair. The brain vasculature exhibits varied spatial
50 – 100 µm in length and 8 – 10 µm in diameter between orientations and metabolic and energy requirements,
25
bifurcations. 7-10 In comparison, the smallest capillaries depending on the brain region (white or gray matter).
in the mouse and rat brains have a diameter of about An essential regulator of the transport of fluid and solutes
3 µm and 4 µm, respectively. Brain capillaries feature along the walls of the cerebral microvasculature is the
11
26
the largest and tightest junctional complexes, whereas mechanical stress exerted by blood flow. Moreover, there
venules have relatively looser junctional configurations. At are significant variations in the density and organization of
27
the level of circumventricular organs (CVOs), capillaries tight junctions along the vascular tree, which influence
are comparatively more permeable, with fenestrations the regions and mechanisms through which chemical
and discontinuous tight junctions (TJs), particularly in macromolecules can enter the brain. The BBB varies in
their central regions. Notably, the CVOs and choroid shape and function across the microvascular network.
plexus (CP) are two vascularized areas of the brain where
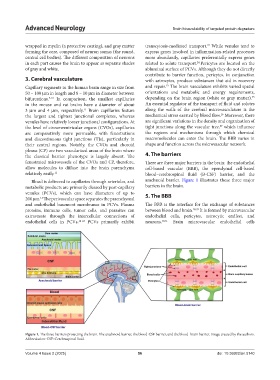
the classical barrier phenotype is largely absent. The 4. The barriers
fenestrated microvessels of the CVOs and CP, therefore, There are three major barriers in the brain: the endothelial
allow molecules to diffuse into the brain parenchyma cell-based vascular (BBB), the ependymal cell-based
relatively easily. 12 blood–cerebrospinal fluid (B-CSF) barrier, and the
Blood is delivered to capillaries through arterioles, and arachnoid barrier. Figure 1 illustrates these three major
metabolic products are primarily cleared by post-capillary barriers in the brain.
venules (PCVs), which can have diameters of up to 5. The BBB
200 µm. The perivascular space separates the parenchymal
13
and endothelial basement membranes in PCVs. Plasma The BBB is the interface for the exchange of substances
proteins, immune cells, tumor cells, and parasites can between blood and brain. 28,29 It is formed by microvascular
extravasate through the intercellular connections of endothelial cells, pericytes, astrocytic endfeet, and
endothelial cells in PCVs. 14-22 PCVs primarily exhibit neurons. 30,31 Brain microvascular endothelial cells
Figure 1. The three barriers protecting the brain. The arachnoid barrier, the blood-CSF barrier, and the blood–brain barrier. Image created by the authors.
Abbreviation: CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid.
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 56 doi: 10.36922/an.5140